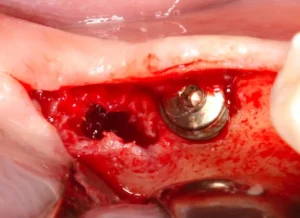
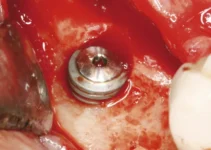
Understanding the causes of dental implant infection is key to maintaining oral health after receiving an implant. Typically, these infections arise from improper post-surgery care, preexisting medical conditions, or inadequate oral hygiene. Bacteria can accumulate around the implant site, leading to peri-implantitis, a condition that affects the gums and bone structure. To prevent such infections, patients are advised to follow strict oral hygiene practices, attend regular dental check-ups, and discuss their medical history with their dental specialist to mitigate risks associated with underlying health issues.
Common Causes of Dental Implant Infection
Dental implants have revolutionized modern dentistry, offering a reliable solution for tooth loss. However, like all surgical procedures, they come with potential risks. One significant concern is the possibility of infection. Understanding the common causes of dental implant infections is crucial for both patients and dentists to ensure long-term success.
By identifying and addressing the underlying factors that contribute to implant-related infections, we can take proactive measures to prevent complications. Below, we discuss some of the most common causes of dental implant infections.
Poor Oral Hygiene
One of the most prevalent causes of dental implant infections is poor oral hygiene. When patients fail to maintain proper oral care, bacteria can accumulate around the implant site. Plaque buildup can lead to peri-implantitis, an inflammatory condition affecting the soft and hard tissues surrounding the implant. This condition is often the precursor to more severe infections.
To mitigate this risk, patients must adhere to a strict oral hygiene regimen, which includes:
- Brushing twice daily with a soft-bristle toothbrush and non-abrasive toothpaste.
- Flossing at least once a day to remove plaque from areas where the toothbrush can’t reach.
- Using an antimicrobial mouthwash to reduce bacterial load.
- Regular dental check-ups for professional cleanings and examinations.
Dentists should provide thorough post-operative instructions and emphasize the importance of maintaining good oral hygiene to their patients.
Pre-existing Medical Conditions
Another significant factor contributing to dental implant infections is the presence of pre-existing medical conditions. Certain systemic diseases, such as diabetes, autoimmune disorders, and osteoporosis, can compromise the body’s ability to heal and fight infections. For instance, patients with uncontrolled diabetes are at a higher risk of developing infections due to impaired immune responses and delayed wound healing.
Before undergoing dental implant surgery, it’s crucial for patients to disclose their full medical history to ensure that any underlying conditions are managed appropriately. Regular monitoring and maintaining control over these conditions can significantly reduce the risk of implant-related infections.
In some cases, pre-surgical evaluations and consultations with the patient’s primary healthcare provider may be necessary to optimize their overall health before proceeding with implant placement.
Improper Implant Placement
Improper implant placement is another common cause of infections. If an implant is placed too close to adjacent teeth or anatomical structures, such as the sinus cavity or nerves, it can create an environment conducive to bacterial growth. Additionally, placing an implant in a site with insufficient bone density can lead to micro-movements, increasing the risk of infection.
To avoid these complications, dentists should conduct a comprehensive examination that includes imaging studies such as CBCT (Cone Beam Computed Tomography) scans. This ensures accurate assessment of the patient’s bone structure and optimal positioning of the implant.
Moreover, employing guided implant surgery techniques can enhance precision during the procedure. Using these advanced methods, dentists can create a surgical guide that directs the exact placement of the implant, minimizing the risk of improper positioning.
By understanding and addressing these common causes of dental implant infections, patients and dental professionals can work together to ensure successful outcomes. For more detailed insights into dental implant care and related topics, explore our other articles. Your journey to a healthier smile doesn’t end here!
Symptoms and Signs of Dental Implant Infection
Dental implant infections, although not exceedingly common, can significantly impact the success of an implant. Recognizing the signs and symptoms early is crucial for timely intervention. Infections can stem from various factors, including poor oral hygiene, peri-implantitis, or systemic health issues. This section will explore the primary symptoms and signs that indicate a dental implant infection. Understanding these symptoms can help both patients and dental professionals make informed decisions and manage complications efficiently. The key is to address these issues promptly to prevent further complications and ensure the longevity of the dental implant.
Swelling and Redness
The most noticeable signs of a dental implant infection are swelling and redness around the implant site. These symptoms indicate inflammation, which is the body’s natural response to infection. Inflammation occurs when the body’s immune system sends an increased supply of blood to the affected area, causing it to appear red and swollen.
Swelling and redness are often accompanied by a feeling of heat around the implant site. Patients may also experience tenderness and discomfort when touching the affected area. This inflammation can extend to the gums and even the cheeks, contributing to a noticeable change in facial appearance.
Persistent Pain
While some discomfort is expected after a dental implant procedure, persistent pain beyond the normal healing period can be a sign of infection. This pain is usually localized around the implant site and can vary in intensity. It may be a dull ache, sharp pain, or throbbing sensation that does not subside with over-the-counter pain medications.
Patients experiencing persistent pain should seek professional evaluation to determine if an infection is present. Addressing this issue early can prevent the spread of infection to the surrounding bone and tissues, which can compromise the stability of the implant and overall oral health.
Pus or Discharge
The presence of pus or discharge around the implant site is a clear indication of infection. Pus is a thick fluid composed of dead white blood cells, bacteria, and tissue debris, signifying that the body is actively fighting an infection. This discharge can have a foul odor and may be accompanied by a bad taste in the mouth.
If not addressed promptly, pus accumulation can lead to an abscess, a painful pocket of infection that can cause significant complications. Proper oral hygiene, regular dental check-ups, and immediate professional care are essential to manage and resolve the infection effectively.
These symptoms are critical for identifying potential dental implant infections early. Patients experiencing any of these signs should consult their dentist immediately. Early intervention can save the implant and prevent further health issues, ensuring the success of the dental procedure.
For more detailed information on dental implant care and other related topics, explore our other articles to stay informed and proactive about your dental health.
Preventing Dental Implant Infections
Dental implants have revolutionized modern dentistry by offering a long-lasting solution for missing teeth. However, like any surgical procedure, there are potential risks, including infections. Preventing dental implant infections is crucial for the longevity and success of the implant. By maintaining excellent oral hygiene and regularly visiting your dentist, you can significantly reduce the risk of infection and ensure the health of your implant.
Recent studies highlight that the incidence of dental implant infections, such as peri-implantitis, can be managed and minimized through proper care protocols. Understanding and implementing these preventive measures is essential for every patient considering or already having dental implants. Let’s explore two key strategies to prevent dental implant infections.
Maintaining Good Oral Hygiene
One of the most effective ways to prevent infections around dental implants is by maintaining good oral hygiene. A daily routine of brushing and flossing can help remove plaque and bacteria that cause infections. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush to avoid damaging the delicate tissue around the implant and choose a toothpaste that is gentle yet effective.
Additionally, incorporating mouthwash into your routine can provide an extra layer of protection. Mouthwashes with antibacterial properties can help reduce the risk of infection by eliminating harmful bacteria in the mouth. It’s also crucial to clean around the implant abutments and prosthetic teeth thoroughly to prevent plaque buildup.
Consider the following tips for maintaining good oral hygiene:
- Brush at least twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush.
- Use floss or interdental brushes designed for implants.
- Rinse with an antibacterial mouthwash daily.
- Avoid smoking, as it can increase the risk of infection and implant failure.
Regular Dental Check-ups
Routine dental check-ups are essential for monitoring the health of your dental implants. Regular visits allow your dentist to identify and address potential issues before they become severe. During these check-ups, your dentist will examine the implant and surrounding tissues, checking for signs of infection or inflammation.
Professional cleanings are another critical aspect of preventing dental implant infections. Dental hygienists possess specialized tools to remove plaque and tartar that cannot be effectively cleaned with regular brushing and flossing. These cleanings are particularly important for implants, as they can harbor bacteria below the gum line. Furthermore, your dentist might recommend periodic X-rays to evaluate the bone around the implant. This helps ensure that the implant remains stable and integrated with the bone. Early detection of any changes can lead to timely intervention, preserving the health of the implant.
By following these preventive measures, you can significantly increase the lifespan and success of your dental implants. For more in-depth information on dental care and advancements in implantology, be sure to explore our other articles.
Common Questions About Dental Implant Infections
Understanding what causes dental implant infections can help in taking preventive steps to ensure the longevity and success of the implant. Here is a commonly asked question:
What are the primary causes of dental implant infections?
Dental implant infections, known as peri-implantitis, can occur due to a variety of factors. These include poor oral hygiene, which allows bacteria to build up around the implant site; smoking, which impairs the body’s ability to heal; inadequate dental procedures or improper placement of the implant; and pre-existing medical conditions, such as diabetes, that can affect the immune response. Managing these risk factors is crucial for preventing infection and ensuring the health of the implant.

My name is Salman Kapa, a 73-year-old expert in bone regeneration and dental implantology. With decades of experience in the field, I am dedicated to advancing our understanding of oral health and hygiene. Through my research and writing, I aim to contribute to the development of innovative solutions in dental care.