Bruxism, commonly known as teeth grinding, poses a significant risk to oral health by causing tooth wear, jaw disorders, and even headaches. Understanding how to effectively detect and manage this condition is crucial for maintaining healthy teeth. Detection typically involves noticing symptoms such as jaw pain, headache, and worn-down teeth, often identified by a dental professional during routine check-ups. Once diagnosed, treatment might include using mouthguards, stress reduction techniques, and sometimes, addressing underlying health issues. This article will explore various strategies to manage bruxism and protect your dental health.
Understanding Bruxism
Bruxism, commonly referred to as teeth grinding or jaw clenching, is a condition that involves the involuntary or habitual grinding of teeth and clenching of the jaw. It can occur both during the day (awake bruxism) and at night (sleep bruxism). According to the American Dental Association, bruxism affects approximately 10% of the population, with many individuals unaware that they even suffer from it. The condition can lead to significant dental and orthodontic issues, such as tooth wear, increased tooth sensitivity, and even tooth fractures.
The exact cause of bruxism is not well understood, but it is believed to result from a combination of physical, psychological, and genetic factors. Stress and anxiety are often cited as major contributors to bruxism, as many people clench or grind their teeth as a coping mechanism. Other potential causes include malocclusion (misaligned teeth), certain medications, and lifestyle factors such as smoking, alcohol consumption, and caffeine intake. To properly diagnose and manage bruxism, dentists often look for signs of tooth wear, gum recession, and jaw muscle hypertrophy. In some cases, a polysomnographic study (sleep study) may be recommended to assess sleep bruxism. Effective treatment strategies commonly involve the following:
- Behavioral interventions such as stress management techniques and biofeedback.
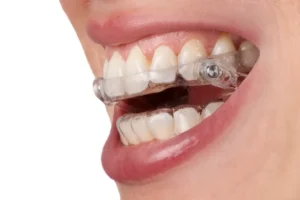
- Dental approaches, including the use of mouthguards or splints to protect teeth.
- Pharmacological treatments aimed at reducing muscular activity or addressing underlying anxiety and stress.
Understanding the underlying causes and potential consequences of bruxism is crucial for effective management. Early intervention can prevent further dental damage and improve the overall quality of life for those affected. If you suspect you have bruxism, it is essential to consult with a dental professional for an accurate diagnosis and customized treatment plan.
How to Detect Bruxism
Bruxism, often referred to as teeth grinding, is a common condition where individuals involuntarily grind or clench their teeth. Detecting bruxism early is crucial to prevent long-term damage to the teeth and jaw. Understanding the signs and symptoms, available diagnostic methods, and knowing when to see a specialist can help manage this condition effectively.
Many people are unaware that they suffer from bruxism as it often occurs during sleep. However, there are several indicators that can help in identifying the presence of this condition. Early detection can avoid complications such as tooth wear, jaw disorders, and even severe headaches.
Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of bruxism can be the first step towards effective management. Common signs include:
- Grinding noise during sleep, often noticed by a sleep partner
- Worn down, flattened, or chipped teeth
- Increased tooth sensitivity due to enamel wear
- Jaw pain or stiffness upon waking
- Chronic headaches, especially in the morning
Some individuals may also experience tired or tight jaw muscles, and in severe cases, lockjaw (difficulty opening or closing the mouth). It is important to pay attention to these symptoms as they can significantly affect oral health over time.
Diagnostic Methods
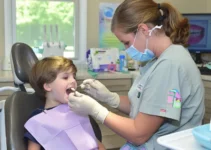
If bruxism is suspected, a dental professional can conduct several diagnostic methods to confirm the condition. These include:
- Dental examination: Checking for signs of tooth wear, sensitivity, and damage that are indicative of bruxism.
- Patient history: Discussing sleep patterns, stress levels, and other factors that might contribute to teeth grinding.
- Monitoring devices: Using devices such as Bruxism Monitors to record teeth grinding activity during sleep.
- X-rays: Evaluating the health of the jaw and any structural damage caused.
These diagnostic tools help in assessing the severity of bruxism and in planning an effective treatment strategy.
It is essential to differentiate between occasional teeth grinding, which may not need intervention, and chronic bruxism, which requires treatment to prevent further complications.
When to See a Specialist
Although occasional teeth grinding is often not harmful, persistent bruxism can lead to serious dental issues and requires professional attention. You should see a specialist if:
- You experience persistent jaw pain or discomfort.
- Your sleep partner complains about the noise created by your teeth grinding.
- You notice damage to your teeth, such as chips, fractures, or increased sensitivity.
- You suffer from chronic headaches or earaches.
A dental specialist can recommend treatment options such as mouthguards, stress management techniques, and in severe cases, medications to reduce muscle activity. Early intervention can greatly improve the quality of life and prevent long-term damage to teeth and jaw joints.
For more in-depth information on oral health conditions and their management, be sure to check out other articles on our site. Stay informed and take control of your dental health today!
Effective Treatment Strategies for Bruxism
Bruxism is a condition characterized by the involuntary grinding or clenching of teeth, most commonly during sleep. It affects both children and adults and can lead to various dental and medical complications if left untreated. Effective treatment strategies for bruxism often involve a combination of approaches tailored to the individual. This article discusses some of the most effective treatment strategies for managing bruxism.
Understanding bruxism is the first step towards effective management. Clinicians often employ comprehensive diagnostic tools to assess the severity and underlying causes of bruxism. Following the diagnosis, a multi-faceted treatment plan can be designed to address the specific needs of the patient. Below, we examine three primary strategies: Behavioral Approaches, Medical Interventions, and Lifestyle Changes.
Behavioral Approaches
Behavioral approaches focus on modifying the habits and behaviors that contribute to bruxism. One effective method is cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), which helps patients understand the emotional and psychological factors behind their teeth grinding. Through CBT, patients can learn to recognize and change the stress-inducing thoughts and behaviors that may trigger bruxism.
Another behavioral approach involves biofeedback therapy. This technique uses various monitoring devices to teach patients how to control involuntary physiological processes such as muscle tension. By understanding these signals, patients can develop better control over their jaw muscles, reducing the frequency and severity of bruxism episodes.
Additionally, patients may benefit from relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, and progressive muscle relaxation. These strategies can help reduce overall stress levels, which is a significant contributor to bruxism. Combining these techniques with consistent practice can lead to long-term improvements.
Medical Interventions
Medical interventions often provide immediate relief from the symptoms of bruxism and can be particularly useful in severe cases. One common intervention is the use of occlusal splints or mouthguards. These devices are custom-fitted to the patient’s mouth and act as a protective barrier, preventing tooth damage during grinding.
In some cases, medication may be prescribed to help manage bruxism. Muscle relaxants can be taken before bedtime to reduce muscle activity during sleep. Additionally, anti-anxiety medications or antidepressants may be prescribed if stress or anxiety are significant contributing factors.
For persistent and severe cases of bruxism, Botox injections may be considered. Botox can help relax the muscles responsible for grinding, thereby reducing the frequency and intensity of bruxism episodes. This treatment should be conducted by a qualified specialist to ensure safety and efficacy.
Lifestyle Changes
Addressing lifestyle factors can also play a crucial role in managing bruxism. Stress management is essential, as stress is a major trigger for teeth grinding. Incorporating regular physical activity, hobbies, and sufficient rest into daily routines can significantly lower stress levels.
Dietary habits also influence bruxism. Reducing the intake of caffeine and alcohol can decrease muscle tension and improve sleep quality, both of which are beneficial in reducing bruxism symptoms. Smoking cessation is another important factor, as nicotine can exacerbate teeth grinding. Creating a relaxing bedtime routine can also help. Activities such as reading, taking a warm bath, or listening to calming music can prepare the body for restful sleep, reducing the likelihood of bruxism. Ensuring an environment conducive to good sleep hygiene, such as a dark, quiet room, can further enhance sleep quality.
By combining behavioral approaches, medical interventions, and lifestyle changes, patients can achieve significant relief from bruxism. It is essential to work closely with healthcare providers to develop and follow a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to individual needs. For more insights into dental health and advanced treatment options, explore our other articles.
FAQ on Bruxism: Detection and Treatment
Understanding Bruxism is crucial for maintaining oral health. Below are some commonly asked questions about how to detect and treat this condition to protect your teeth.
What are the primary symptoms of Bruxism?
The primary symptoms of Bruxism include teeth grinding or clenching, which often occurs during sleep, leading to disrupted sleep patterns. Other symptoms may involve jaw pain or tightness, increased tooth sensitivity, and erosion of enamel that can lead to further dental damage. It’s important to be aware of these signs as early detection can help prevent more serious damage.
What are the effective treatment options for Bruxism?
Treatment for Bruxism hinges on the severity of the condition but commonly involves the use of a night guard to prevent teeth grinding and clenching during sleep. Additionally, managing stress through relaxation techniques or therapy can be effective, as stress is a significant contributing factor to Bruxism. In severe cases, dental correction or muscle relaxants might be prescribed by a healthcare provider.

My name is Salman Kapa, a 73-year-old expert in bone regeneration and dental implantology. With decades of experience in the field, I am dedicated to advancing our understanding of oral health and hygiene. Through my research and writing, I aim to contribute to the development of innovative solutions in dental care.