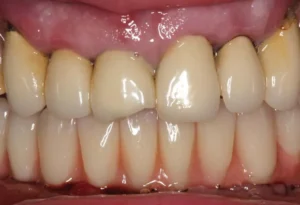
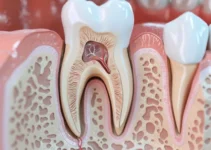
The longevity of dental bridges is a common concern among patients considering or currently using them as a solution for missing teeth. Typically, a well-maintained dental bridge can last anywhere from 5 to 15 years, depending on various factors such as the material used, the quality of the installation, and the patient’s oral hygiene practices. Regular dental check-ups and proper care are essential to maximize the lifespan of a dental bridge, helping ensure that it remains functional and aesthetically pleasing for as long as possible.
Factors Affecting the Duration of Dental Bridges
The longevity of dental bridges, a popular solution for missing teeth, is influenced by several key factors. Understanding these factors can help both patients and dental professionals make informed decisions about dental care and maintenance. In this article, we will explore the impact of material quality, oral hygiene, and diet and lifestyle on the durability of dental bridges.
By addressing these aspects, patients can potentially prolong the lifespan of their dental bridges, ensuring a healthier and more aesthetic smile over the years. Let’s delve into these factors in more detail to understand their significance.
Material Quality
The quality of materials used in making dental bridges significantly influences their lifespan. High-quality materials such as porcelain fused to metal (PFM), zirconia, and gold alloys are known for their durability and aesthetic appeal. Porcelain, for instance, mimics the natural appearance of teeth, while zirconia offers superior strength and durability.
Different materials have varying degrees of wear resistance and biocompatibility. For example:
- Porcelain: High aesthetic value but can be prone to chipping.
- Zirconia: Durable and resistant to fractures, ideal for patients with heavy biting forces.
- Gold alloys: Highly biocompatible and resistant to corrosion, though less common due to their metallic appearance.
Choosing the right material involves a careful assessment of the patient’s specific needs and the location of the bridge in the mouth. A thorough discussion with a dental professional is essential for making an informed choice.
Oral Hygiene
Maintaining excellent oral hygiene is crucial for the longevity of dental bridges. Brushing twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste and daily flossing help remove plaque and food particles that can lead to gum disease and decay, both of which can compromise the stability of a dental bridge.
Patients should also consider using interdental brushes or water flossers to clean around and under the bridge. Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings are essential to monitor the health of the bridge and surrounding teeth and gums.
Neglecting oral hygiene can lead to complications such as:
- Gum disease: Inflammation and infection of the gums can weaken the support for the dental bridge.
- Cavities: Decay in the supporting teeth can compromise the bridge’s stability.
- Bone loss: Poor oral hygiene can lead to bone loss around the supporting teeth, affecting the bridge’s fit and stability.
Diet and Lifestyle
Diet and lifestyle choices can also impact the lifespan of a dental bridge. Consuming a diet high in sugary and acidic foods can contribute to tooth decay and gum disease, which in turn affects the stability of a bridge. It is recommended to minimize sugary snacks and drinks, and to maintain a balanced diet rich in vegetables, fruits, and calcium-rich foods.
Avoiding hard foods such as ice, nuts, and hard candies can prevent damage or fractures to the bridge. Habits like bruxism (teeth grinding) can also exert excessive pressure on a dental bridge. In such cases, patients might benefit from protective measures such as wearing a night guard.
Lifestyle factors such as smoking can have a detrimental impact on oral health. Smoking not only stains teeth but also impairs the healing process and increases the risk of periodontal disease, which can undermine the support for a dental bridge.
Making conscious choices about diet and lifestyle can significantly enhance the longevity of dental bridges, contributing to overall oral health and well-being.
Understanding these factors is crucial for anyone considering or currently using a dental bridge. By prioritizing material quality, maintaining rigorous oral hygiene, and making healthy lifestyle choices, patients can ensure the long-term success of their dental bridges. For more in-depth information on related topics, explore our other articles on dental health and maintenance.
Types of Dental Bridges and Their Lifespan
Dental bridges are a popular solution for replacing missing teeth. They help restore function and aesthetics, and there are different types suited for various dental situations. Knowing the different types and their lifespans can help patients make informed decisions about their oral health.
Dental bridges generally have a lifespan of 5 to 15 years, but this can vary depending on the type of bridge, the material used, and how well the patient maintains their oral hygiene. Below, we explore three common types of dental bridges and discuss their specific characteristics and expected lifespans.
Traditional Dental Bridges
Traditional dental bridges are the most common type, usually consisting of one or more artificial teeth held in place by dental crowns cemented onto adjacent natural teeth. These crowns act as anchors, providing stability and strength to the bridge.
The lifespan of traditional dental bridges is typically between 10 to 15 years. However, with excellent oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups, they can last even longer. Factors that can influence their durability include the patient’s bite, the materials used (such as porcelain, ceramic, or metal), and the overall health of the supporting teeth.
Traditional bridges are ideal for patients who have strong, healthy teeth adjacent to the gap left by the missing tooth. They provide excellent function and aesthetics, closely mimicking the appearance of natural teeth. However, one downside is that the adjacent teeth need to be filed down to accommodate the crowns, which can compromise their structure.
Cantilever Dental Bridges
Cantilever dental bridges are similar to traditional bridges but are supported by a crown on only one side. They are used when there are no teeth on one side of the missing tooth, requiring less preparation of neighboring teeth.
The lifespan of cantilever bridges is slightly shorter, generally lasting between 7 to 10 years. This is because the cantilever structure places more stress on the supporting tooth. Ensuring good oral hygiene and avoiding excess force on the bridge, such as from chewing hard foods, can help prolong its lifespan.
These bridges are best suited for front teeth where the forces of biting and chewing are less intense compared to the molars. While they can effectively restore appearance and function, patients must be vigilant about maintaining oral hygiene to avoid complications like decay or gum disease around the supporting tooth.
Maryland Bonded Bridges
Maryland bonded bridges, also known as resin-bonded bridges, consist of a metal or porcelain framework with artificial teeth attached. This framework is bonded to the back of adjacent natural teeth using a resin, avoiding the need for crowns. Maryland bridges typically last between 5 to 8 years. They are less invasive than traditional or cantilever bridges because they do not require significant alteration to the adjacent teeth. However, their durability can be affected by the resin bonding material, which may wear down over time.
These bridges are usually recommended for front teeth, where the stress of chewing is minimal. They offer a conservative approach to replacing missing teeth and preserve much of the natural tooth structure. However, they might not be suitable for everyone, especially in cases where the adjacent teeth are not strong enough to support the bridge.
Understanding the different types of dental bridges and their lifespans can help you make an educated decision about your dental care. Make sure to consult with a dental professional to determine the best option for your specific needs. If you found this article helpful, read more on our website to explore other dental solutions and tips for maintaining optimal oral health.
Extending the Lifespan of Your Dental Bridge
Dental bridges are an effective and aesthetically pleasing solution for replacing missing teeth. However, like any dental appliance, they require proper care and maintenance to ensure they last as long as possible. By following a few key practices, you can significantly extend the lifespan of your dental bridge and maintain a bright, healthy smile.
One of the most important steps in extending the lifespan of your dental bridge is to commit to regular dental visits and proper hygiene practices. By doing so, you can prevent many common issues that may arise with dental bridges, such as decay and gum disease. In this article, we’ll explore some essential tips for maintaining your dental bridge.
Routine Dental Check-ups
One of the most critical components of maintaining your dental bridge is scheduling routine dental check-ups. Regular visits to your dentist allow for the early detection of any potential problems, ensuring they are addressed before they become serious. Your dentist will thoroughly check the condition of the bridge, the supporting teeth, and the surrounding gum tissue.
During these check-ups, your dentist may also perform professional cleanings to remove plaque and tartar buildup, which are common culprits in dental issues. They can provide personalized advice on how to care for your dental bridge and adjust any misalignments or irregularities that could lead to complications.
Proper Cleaning Techniques
Maintaining good oral hygiene is pivotal for the longevity of your dental bridge. It’s important to follow proper cleaning techniques to prevent plaque buildup and decay around the bridge and supporting teeth. Here are some key practices for effective cleaning:
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day using a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Be gentle around the bridge area to avoid damaging it.
- Use an interdental brush or floss threader to clean between the bridge and supporting teeth, where regular brushes might not reach.
- Consider using an antiseptic mouthwash to help reduce plaque and bacteria.
By integrating these techniques into your daily oral hygiene routine, you can help protect your dental bridge from the common issues that compromise its integrity.
Avoiding Harmful Habits
Certain habits can greatly diminish the lifespan of your dental bridge. It is essential to be mindful of actions that exert undue stress on your bridge. Avoiding harmful habits can prevent unnecessary damage and ensure your bridge remains functional and aesthetically pleasing. Some detrimental habits to avoid include:
- Using your teeth as tools to open packaging or bottles can lead to chips and cracks.
- Chewing on hard objects like ice, pen caps, or fingernails can weaken or fracture the bridge.
- Consuming excessive sugary foods and drinks can increase the risk of decay around the supporting teeth.
By being conscious of these habits and making efforts to avoid them, you can extend the durability and effectiveness of your dental bridge.
In conclusion, extending the lifespan of your dental bridge requires a combination of regular dental check-ups, proper cleaning techniques, and avoiding harmful habits. By taking these steps, you can enjoy the benefits of your dental bridge for many years to come. For more insights into dental care and oral health, be sure to read our other articles.
Dental Bridge Duration FAQs
Explore commonly asked questions about the durability and lifespan of dental bridges, helping you understand what to expect from this dental solution.
How long does a dental bridge typically last?
A dental bridge can last between 5 to 15 years, and sometimes even longer with proper care and maintenance. Factors affecting its lifespan include the material used, the health of surrounding teeth, and oral hygiene practices.

My name is Salman Kapa, a 73-year-old expert in bone regeneration and dental implantology. With decades of experience in the field, I am dedicated to advancing our understanding of oral health and hygiene. Through my research and writing, I aim to contribute to the development of innovative solutions in dental care.