Dental implant gum problems can occur due to a variety of factors including improper oral hygiene, infections, or even the natural aging process. These issues are not only discomforting but can also affect the longevity and functionality of your implants. Understanding the signs such as redness, swelling, and bleeding around the implant site early on can lead to more effective management. This article delves into common gum complications associated with dental implants and offers practical advice to maintain optimal oral health and ensure the durability of your implants.
Common Gum Problems Associated with Dental Implants
Dental implants have revolutionized restorative dentistry by providing a permanent solution for missing teeth. Nonetheless, like any medical procedure, they come with potential complications. Among the most concerning are gum problems that can compromise the success and longevity of the implants. Understanding these issues is critical for both patients and practitioners.
While dental implants themselves are highly durable and effective, the surrounding gum tissue can sometimes suffer from various issues. These problems can range from mild inflammation to more severe conditions that might even result in implant failure. It’s essential to identify and address these concerns promptly to ensure the best outcomes for the patient.
Peri-Implantitis
Peri-Implantitis is a severe condition characterized by the inflammation of the gum tissue and the bone surrounding a dental implant. This condition can lead to the loss of supporting bone and potentially cause the implant to fail. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to preventing significant damage.
Studies indicate that peri-implantitis affects about 10% of dental implant patients. The primary causes include poor oral hygiene, smoking, and uncontrolled diabetes. Symptoms may include bleeding gums, pus discharge, and deepening of the gingival pockets around the implant.
To manage peri-implantitis, treatment options include mechanical debridement, antibiotic therapy, and surgical interventions to regenerate lost bone and soft tissues. Patients are advised to maintain excellent oral hygiene and attend regular follow-up visits to monitor the health of their implants.
Gum Recession
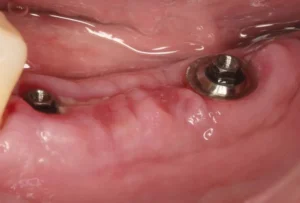
Gum recession around dental implants is another common issue. This occurs when the gum tissue around the implant starts to pull away, exposing the metal post. While it may not be painful initially, gum recession can lead to more severe problems if left untreated.
The primary causes of gum recession include aggressive brushing, periodontal disease, and trauma from improperly fitting dental prostheses. Symptoms can include sensitivity to hot and cold, a noticeable elongation of the implant post, and aesthetic concerns due to visible metal.
Management of gum recession involves both non-surgical and surgical treatments. Non-surgical options might include altering brushing techniques and improving oral hygiene. Surgical interventions could involve grafting procedures that aim to restore the lost gum tissue around the implant, thereby providing both functional and aesthetic benefits.
Inflammation and Swelling
Inflammation and swelling of the gum tissue around a dental implant are often early signs of more serious problems like peri-implantitis. These symptoms can occur soon after the implant procedure or may develop gradually over time.
Common causes of gum inflammation and swelling include plaque buildup, infections, and allergic reactions to the implant material. Symptoms might include redness, tenderness, and a feeling of tightness around the affected area.
Treating inflammation and swelling promptly is essential to prevent further complications. Immediate steps often involve professional cleaning and the use of antibacterial mouth rinses. In more severe cases, antibiotics and minor surgical interventions may be necessary to address the underlying cause.
Patients should be educated on the importance of maintaining excellent oral hygiene and attending regular dental check-ups to monitor the health of their gums and implants. Early detection and treatment can avert more serious complications and ensure the longevity of the dental implants.
Understanding these common gum problems associated with dental implants is crucial for both patients and dental professionals. For further insights into dental implant care and other related topics, consider exploring our other articles.
Preventive Measures for Healthy Gums
Maintaining healthy gums is crucial not only for oral health but also for overall well-being. Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, can lead to severe complications, including tooth loss and has even been linked to systemic health issues such as heart disease and diabetes. Fortunately, many of these complications can be prevented with proper oral care and regular dental check-ups.
In this article, we will explore some effective preventive measures to ensure that your gums remain healthy. We’ll delve into the importance of proper oral hygiene and the significance of regular dental check-ups. By following these guidelines, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing gum disease.
Proper Oral Hygiene
Proper oral hygiene is the cornerstone of preventing gum disease. Brushing your teeth at least twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste is essential. Brushing removes food particles and plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—from the surface of your teeth and gums. Make sure to use a toothbrush with soft bristles and replace it every three to four months or sooner if the bristles become frayed.
Flossing daily is equally important as it helps remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth and under the gumline, areas where your toothbrush can’t reach. Some people find it helpful to use interdental brushes or water flossers for this purpose. Remember, the goal is to disrupt the plaque biofilm and prevent it from hardening into tartar, which can only be removed by a dental professional.
Using an antimicrobial mouthwash can also be beneficial. Mouthwashes can help reduce the bacteria in your mouth and can be an excellent addition to your oral hygiene routine. Look for a product that has the American Dental Association (ADA) seal of approval to ensure its efficacy.
Regular Dental Check-Ups
Regular dental check-ups are indispensable for maintaining healthy gums. During these visits, your dentist will perform a thorough examination of your mouth, including checking for signs of gum disease. Early detection of problems can save you from more complex and costly treatments later on.
Professional dental cleanings, which are a part of regular check-ups, are essential for removing plaque and tartar that your everyday brushing and flossing might miss. These cleanings can prevent gum inflammation and progression to more severe periodontal disease. Most dental professionals recommend visiting your dentist every six months. However, if you have a history of gum disease or other oral health issues, more frequent visits may be necessary. Your dentist can provide personalized advice on how often you should come in for check-ups.
In addition to professional care, your dentist can also provide valuable advice on improving your at-home oral care routine. They may recommend specific tools like electric toothbrushes, floss holders, or even changes in your diet to enhance your gum health.
Consistent preventive measures can go a long way in ensuring not just the health of your gums, but your overall well-being. If you found this article helpful, don’t hesitate to explore our other articles on dental care and oral health best practices.
Treatment Options for Gum Problems
Gum problems, often manifesting as gingivitis or periodontitis, are prevalent oral health issues that demand immediate attention. The treatment options vary based on the severity of the condition and range from non-surgical approaches to more invasive procedures. Understanding these options can help in choosing the most effective treatment plan. This section will explore two primary treatments: professional cleaning and surgical interventions, highlighting their importance and procedures involved.
Early intervention is crucial in treating gum problems to prevent further complications such as tooth loss or systemic health issues. Treatment efficacy significantly improves with timely and appropriate care, and the prognosis for gum health can be optimistic when treatment is started early. Let’s delve into the specifics of these treatment options.
Professional Cleaning
Professional dental cleaning, also known as prophylaxis, is the first line of defense against gum diseases. It involves the removal of dental plaque and tartar that cannot be eliminated by regular brushing and flossing. This procedure is essential for maintaining optimal gum health and preventing the progression of gingivitis to periodontitis. Regular professional cleaning is recommended every six months for most individuals, though those with higher risk factors may need more frequent cleanings. The procedure typically includes scaling and polishing. Scaling removes plaque and tartar from the tooth surfaces, especially below the gum line, while polishing smoothens the teeth to prevent future plaque accumulation. Research has shown that regular professional cleanings can reduce the incidence of periodontal disease significantly.
Professional cleanings also allow dentists to spot early signs of gum disease and other oral health issues, enabling timely intervention. This proactive approach not only maintains oral health but also supports overall health, as oral health is closely linked to systemic conditions such as diabetes and heart disease.
Surgical Interventions
When gum disease has progressed to a more advanced stage, surgical interventions may be necessary to restore oral health. These procedures aim to remove the disease-causing bacteria, reduce pockets, and regenerate lost tissues. Common surgical options include flap surgery, bone grafts, and soft tissue grafts.
Flap surgery (or pocket reduction surgery) involves lifting back the gums to remove tartar deposits deep beneath the gum line. This procedure reduces the pocket size, making it easier to maintain oral hygiene. Bone grafts are used to regenerate bone lost due to periodontal disease. This procedure involves using fragments of your own bone, synthetic bone, or donated bone to replace lost bone. Soft tissue grafts help cover exposed roots and reinforce thin gums, enhancing both oral health and aesthetics.
Studies indicate that surgical interventions, when combined with ongoing maintenance and professional care, can significantly improve the long-term prognosis of patients with severe gum disease. These procedures are meticulously planned and executed to ensure the best possible outcomes for gum health.
It’s important to discuss with your dentist or periodontist to determine the most suitable treatment plan based on your specific condition. Surgery is typically considered when non-surgical treatments and professional cleanings are insufficient to control the disease.
For further information on maintaining optimal oral health and exploring the latest advancements in dental care, consider reading our other articles on dental hygiene and advanced periodontal treatments.
Post-Treatment Care and Maintenance
Once you have undergone dental implant surgery, post-treatment care and maintenance are crucial to ensure the long-term success of your implants. Neglecting these aspects can lead to complications such as infections or implant failure. Proper care includes not only maintaining good oral hygiene but also making certain lifestyle changes and attending regular follow-up appointments.
By following your dentist’s instructions diligently, you can maximize the lifespan of your dental implants. This article will delve into essential lifestyle changes and the importance of follow-up appointments to ensure the health and longevity of your implants.
Lifestyle Changes
After dental implant surgery, certain lifestyle changes can significantly impact the success of your treatment. One of the most critical adjustments is to maintain excellent oral hygiene. Brushing and flossing regularly helps to keep your mouth free of harmful bacteria that can cause infections around the implant site. Additionally, using an antimicrobial mouthwash can further reduce the risk of infection.
Avoiding smoking is another crucial lifestyle change. Smoking can impede healing and increase the risk of implant failure. Studies have shown that smokers have a higher rate of implant complications compared to non-smokers. Therefore, if you smoke, consider quitting to improve your chances of a successful implant.
Dietary habits also play a role in the success of your dental implants. Consuming a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports your body’s natural healing processes. Avoiding hard or sticky foods can prevent unnecessary stress on your implants during the initial healing phase.
Follow-Up Appointments
Regular follow-up appointments with your dentist are essential for monitoring the health of your dental implants. These appointments allow your dentist to assess the osseointegration process, which is the bonding of the implant to the jawbone. Any issues can be detected early and addressed promptly.
During follow-up visits, your dentist will also check for signs of inflammation or infection around the implant site. Early detection of these issues can prevent more severe complications down the line. Additionally, your dentist can provide professional cleaning to remove plaque and tartar buildup that regular brushing and flossing might miss.
These appointments also serve as an opportunity for you to ask questions or express any concerns you may have about your implants. Your dentist can provide personalized advice and recommendations tailored to your specific needs.
In summary, post-treatment care and maintenance are vital for the success of dental implants. By making necessary lifestyle changes and attending regular follow-up appointments, you can ensure that your implants remain healthy and functional for years to come.
If you found this information helpful, be sure to check out our other articles on dental health and implantology for more insights and tips.
Common Questions About Dental Implant Gum Problems
Understanding the issues related to gums around dental implants is crucial for maintaining oral health. Here’s a frequently asked question on this topic.
What are the signs of gum problems around dental implants?
Gum problems around dental implants, often known as peri-implant diseases, can manifest as redness, swelling, pain, or bleeding when brushing or flossing around the implant. Another common sign is the receding gum line around the implant, which might expose the metal base. If you notice any pus or feel that the implant is wobbly, it’s essential to contact your dentist immediately as these could be signs of infection that require prompt treatment.

My name is Salman Kapa, a 73-year-old expert in bone regeneration and dental implantology. With decades of experience in the field, I am dedicated to advancing our understanding of oral health and hygiene. Through my research and writing, I aim to contribute to the development of innovative solutions in dental care.