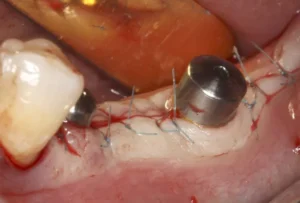
Dental implant pus is a concerning sign that may indicate an infection around a dental implant. This condition, commonly known as peri-implantitis, is typically caused by bacteria buildup that can lead to inflammation and damage to surrounding tissues. Early detection and treatment are vital to preserve the implant and maintain overall oral health. This article delves into the origins of dental implant pus, effective prevention strategies, and the latest treatment options to manage this dental complication.
Causes of Pus Formation in Dental Implants
Dental implants are a revolutionary solution for tooth loss, offering a durable and natural-looking replacement option. However, complications can arise, including the formation of pus around the implant site. This could be a sign of infection and is a matter of concern for both patients and practitioners. Understanding the causes behind pus formation can help in preventing and managing these complications effectively.
Several factors can contribute to pus formation around dental implants, primarily related to bacterial infection and poor oral hygiene. In this section, we will explore these causes in detail, providing insights into their role in the development of complications associated with dental implants.
Infection and Bacterial Contamination
One of the primary causes of pus formation around dental implants is infection due to bacterial contamination. The mouth is naturally home to a wide variety of bacteria. When a dental implant is placed, it creates an environment where bacteria can potentially thrive if not appropriately managed. Studies have shown that bacterial biofilms, which are communities of bacteria adhering to surfaces, can form on the dental implant and surrounding tissues, leading to infection.
Bacterial contamination can occur during the surgery, from instruments, or even from the oral cavity itself. It’s important to maintain sterile conditions during the implant procedure to minimize the risk of infection. After the procedure, the implant site can become a target for bacteria, especially if there is any damage to the surrounding gum or bone.
Symptoms of infection may include swelling, redness, and pus discharge. Timely intervention is crucial to prevent the infection from spreading and causing more severe complications. Treatment often involves antibiotics and may require surgical intervention to clean the infected area.
Poor Oral Hygiene
Maintaining excellent oral hygiene is essential for the health and longevity of dental implants. Poor oral hygiene can lead to a build-up of plaque and tartar around the implant, creating an ideal environment for bacterial growth. This build-up can result in gum inflammation and infection, known as peri-implantitis, which can cause pus formation.
Patients with dental implants need to follow rigorous cleaning routines, including brushing, flossing, and possibly using antibacterial mouth rinses. Regular dental check-ups are also crucial. Dentists can provide professional cleaning and monitor the health of the implant and surrounding tissues, ensuring any early signs of problems are addressed promptly.
It’s essential to educate patients on the importance of oral hygiene and provide them with specific instructions tailored to their needs. This may include the use of specialized cleaning tools designed for implants. Consistent and proper oral care can significantly reduce the risk of complications and enhance the success rate of dental implants.
In summary, understanding the causes of pus formation around dental implants is key to effective prevention and treatment. Infection and poor oral hygiene are major contributors, and addressing these issues through proper surgical techniques and patient education can greatly improve implant outcomes. For more information on maintaining dental implant health, consider exploring our other articles on peri-implantitis prevention and advanced oral care techniques.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Understanding the symptoms and diagnostic procedures for dental issues, particularly those involving infections and potential complications, is crucial for effective treatment and patient care. Early detection and accurate diagnosis can help prevent further damage and ensure timely intervention.
Dental infections can manifest through various symptoms, some of which are visible, while others require professional assessment. Let’s delve into the common signs of infection, the diagnostic procedures used by dental professionals, and a clear definition of dental pus.
Visible Signs of Infection
Visible signs of infection in the oral cavity are often the first indicators that there might be an underlying issue. Patients may notice redness and swelling in the affected area, which can be accompanied by pain or tenderness. These symptoms are commonly seen in cases of gum disease, abscesses, or other oral infections.
Another common visible sign is the presence of white or yellowish lesions, which could indicate the accumulation of pus due to a bacterial infection. Bad breath or an unpleasant taste in the mouth can also be symptomatic of an infection, particularly if these symptoms persist despite good oral hygiene.
In more severe cases, patients may experience bleeding gums, loose teeth, or even an inability to open their mouth fully due to swelling. It’s important for patients to seek dental attention when they notice these signs to prevent the infection from spreading or causing further complications.
Diagnostic Procedures
To accurately diagnose dental infections and underlying conditions, dental professionals utilize a combination of clinical examination and diagnostic tools. One of the primary methods is a thorough visual and tactile examination of the oral cavity. During this examination, the dentist will check for signs of inflammation, swelling, and the presence of pus or abscesses. Radiographic imaging, such as X-rays, is another essential diagnostic tool. X-rays can reveal the extent of the infection, showing any bone loss, the presence of abscesses, or other abnormalities that may not be visible to the naked eye. This imaging helps in planning the appropriate course of treatment.
In some cases, the dentist may also perform a bacterial culture or sensitivity test. This involves taking a sample from the infected area and analyzing it to identify the specific type of bacteria causing the infection. Knowing the exact bacteria can help in selecting the most effective antibiotic treatment.
Other diagnostic methods might include thermal tests to assess the vitality of the teeth and periodontal probing to measure pocket depths around teeth and evaluate the health of the surrounding gum tissue.
Definition of Dental Pus
Dental pus is a thick, yellowish or white fluid that accumulates as a result of a bacterial infection within the tissues of the oral cavity. It is composed of dead white blood cells, bacteria, and tissue debris. The presence of pus indicates that the body is fighting an infection and that there is an ongoing inflammatory response.
The formation of pus is typically associated with dental abscesses, which can occur at the root of a tooth (periapical abscess), in the gums (periodontal abscess), or in the tissues surrounding a tooth (pericoronal abscess). Symptoms of a dental abscess include severe pain, swelling, fever, and tenderness in the affected area.
It is crucial to seek immediate dental care if pus is detected, as untreated abscesses can lead to more serious health complications, such as the spread of the infection to other parts of the body, including the jawbone, neck, or even the brain.
For more detailed information on managing dental infections and other related topics, be sure to read our other articles. Exploring these resources will provide a broader understanding and help you maintain optimal oral health.
Prevention and Treatment
Prevention and treatment of dental issues, especially those pertaining to implantology and bone regeneration, are crucial for maintaining optimal oral health. Proper preventative measures can significantly reduce the risk of complications, while effective treatments can address issues early on, preventing further deterioration. This section will delve into regular dental check-ups, proper oral hygiene techniques, and antibiotic therapy as pivotal aspects of prevention and treatment in dental care.
A comprehensive approach to dental care involves not only the treatment of existing problems but also the implementation of preventive strategies to avert future issues. By adhering to a combination of professional guidance and personal care routines, patients can enjoy long-term dental health. Let’s explore some of the key practices.
Regular Dental Check-Ups
One of the most essential components of dental prevention is scheduling regular check-ups. These visits allow dentists to monitor oral health, identify potential problems early, and administer necessary treatments promptly. Regular dental appointments play a pivotal role in maintaining both natural teeth and dental implants.
During these check-ups, a dentist will conduct a thorough examination, which includes looking for signs of gum disease, cavities, and other oral health issues. Additionally, they often perform professional cleanings to remove plaque and tartar that regular brushing and flossing might miss. This routine maintenance is critical in preventing more serious problems.
Furthermore, regular dental check-ups are particularly important for patients with dental implants. They enable the dentist to ensure that the implants are integrating well with the jawbone and that there are no signs of infection or other complications. Consistent monitoring helps in maintaining the longevity and functionality of dental implants.
Proper Oral Hygiene Techniques
Implementing proper oral hygiene techniques is fundamental in preventing dental issues. Essential practices include brushing at least twice a day, flossing daily, and using mouthwash to reduce bacteria. These habits help in maintaining a clean and healthy oral environment. For individuals with dental implants, maintaining impeccable oral hygiene is even more critical. Implants, like natural teeth, can be susceptible to plaque buildup and infection if not properly cared for. Special brushes and floss designed for implants can be particularly useful in ensuring thorough cleaning.
Using a fluoride toothpaste can also help strengthen the enamel of natural teeth and protect against decay. Additionally, it is recommended to replace toothbrushes every three to four months or sooner if the bristles are frayed. Consistency in these practices significantly reduces the risk of oral health problems.
Antibiotic Therapy
Antibiotic therapy can be a vital component in the treatment of certain dental conditions, particularly when infections are present. These medications are used to target and eliminate bacterial infections, preventing the spread and reducing the risk of further complications.
In the context of dental implants, antibiotics might be prescribed pre- and post-operatively to minimize the risk of infection during the healing process. The use of antibiotics helps to ensure that the surgical site remains free of harmful bacteria that could jeopardize the success of the implant.
It is important to use antibiotics strictly as prescribed by a dental professional. Overuse or improper use can lead to antibiotic resistance, making infections harder to treat in the future. Therefore, adherence to the prescribed dosage and duration is crucial.
While antibiotics can be highly effective, they are typically part of a broader treatment plan that includes good oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups. By combining these approaches, patients can effectively manage and prevent oral health issues.
To deepen your understanding of how to maintain optimal oral health and explore various treatment options, be sure to read our other articles on related topics. Knowledge is power when it comes to achieving and maintaining a healthy smile.
Frequently Asked Questions About Dental Implant Pus
If you are noticing issues with your dental implant, such as pus formation, you might have several questions. Here, we cover some essential inquiries to help you understand what pus around a dental implant signifies, and how it should be addressed.
What causes pus around a dental implant and how is it treated?
Pus around a dental implant is typically the result of an infection known as peri-implantitis. This condition arises from the accumulation of bacteria at the implant site, which can happen due to poor oral hygiene, smoking, or the presence of pre-existing health conditions that affect the gums. Treatment generally involves deep cleaning of the affected area, possibly accompanied by antibiotics to eliminate the infection, and sometimes surgical intervention to remove any damaged tissue and ensure the implant’s health and stability.

My name is Salman Kapa, a 73-year-old expert in bone regeneration and dental implantology. With decades of experience in the field, I am dedicated to advancing our understanding of oral health and hygiene. Through my research and writing, I aim to contribute to the development of innovative solutions in dental care.