Dental implant rejection is a rare but concerning issue for patients undergoing dental restoration. Understanding why it happens is crucial for both patients and clinicians. Typically, rejection might occur due to factors like inadequate oral hygiene, autoimmune responses, or the incompatibility of the implant material with the patient’s body. This article delves into the various causes of dental implant rejections, exploring how patients can work closely with their dentists to minimize risks and ensure the long-term success of their dental implants.
Introduction to Dental Implant Rejection
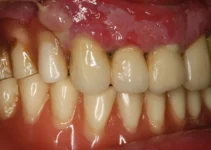
Dental implants have revolutionized modern dentistry, offering a durable and aesthetically pleasing solution for tooth loss. Despite their high success rates, it’s crucial to understand that complications can arise. One such complication is dental implant rejection. This article aims to shed light on what dental implant rejection is, how to identify it, and common misconceptions surrounding the topic.
Understanding dental implant rejection helps both patients and professionals manage expectations and outcomes better. Awareness is the first step to prevention and effective management. Let’s delve into the specifics of dental implant rejection.
What is Dental Implant Rejection?
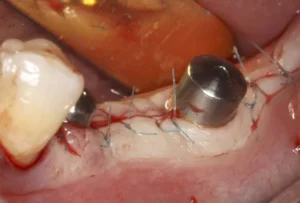
Dental implant rejection occurs when the body identifies the implant as a foreign object and initiates an immune response against it. This is relatively rare, thanks to advancements in materials and surgical techniques, but it remains a possibility. The implants are usually made of biocompatible materials like titanium, which blends well with bone tissue.
However, in some instances, the body may not accept the implant, leading to rejection. It is essential to distinguish between rejection and other complications like infections or poor osseointegration. Proper diagnosis is crucial to determining the right course of action.

Key factors that may contribute to dental implant rejection include poor surgical technique, smoking, uncontrolled diabetes, and history of radiation therapy in the implant area. These factors compromise the healing process and increase the likelihood of rejection.
Signs and Symptoms of Rejection
Identifying the signs and symptoms of dental implant rejection early can make a significant difference in treatment outcomes. Common indicators include:
- Persistent pain or discomfort around the implant area.
- Inflammation or swelling that does not subside with time or medication.
- Mobility of the implant, indicating it has not properly fused with the bone.
- Pus or other signs of infection around the implant site.
These symptoms may overlap with other dental issues, making professional evaluation necessary. Diagnostic tools such as X-rays and CT scans can help confirm whether the implant is being rejected or if another issue is at play.
Prompt identification and intervention can often mitigate the impact of rejection, allowing for alternative treatments or correctional procedures. It’s essential to follow up regularly with your dental professional to monitor the implant site.
Common Misconceptions
Several misconceptions surround dental implant rejection. One widespread myth is that rejection is solely due to the body’s autoimmune response. While the immune system does play a role, factors like surgical technique and patient health are equally significant.
Another misconception is that once an implant is rejected, no further implants can be placed. In reality, patients can often receive new implants after addressing underlying issues that led to the initial rejection. Factors such as bone health, infection control, and overall health must be reviewed before attempting a new implant. Lastly, some believe that dental implant rejection indicates poor quality of the implant material, which is not necessarily true. Most dental implants are made from high-quality, biocompatible materials. The key lies in proper placement and patient-specific considerations.
Understanding these misconceptions helps patients have a more realistic outlook on dental implant procedures and manage their expectations effectively. For more insights, consider reading our other articles on related topics.
Causes of Dental Implant Rejection
Dental implants have transformed the field of dentistry by providing a reliable solution for replacing missing teeth. However, like any medical procedure, there are risks involved. One significant concern is the potential for implant rejection. Understanding the causes of dental implant rejection can help both patients and professionals take preventive measures. In this section, we will explore the primary factors that contribute to implant failure. Rejection of dental implants can be influenced by various factors, ranging from biological responses to surgical complications and material incompatibility. Each of these factors plays a critical role in determining the success or failure of an implant procedure. Let’s delve deeper into each of these causes.
Biological Factors
Biological factors are often a leading cause of dental implant rejection. One primary factor is insufficient bone density. For an implant to successfully integrate with the jawbone, there must be adequate bone mass to support it. Patients with osteoporosis or other conditions that reduce bone density are at a higher risk for implant failure.
Another critical biological factor is infection. Peri-implantitis, an inflammatory condition affecting the soft and hard tissues surrounding the dental implant, can lead to implant rejection. Infection can stem from poor oral hygiene, bacterial contamination during surgery, or a patient’s preexisting medical conditions, such as diabetes.
Lastly, the body’s immune response can also play a vital role. Some individuals may have an adverse immunological reaction to the implant, viewing it as a foreign object. This reaction can trigger inflammation and hinder the osseointegration process, ultimately leading to implant failure.
Surgical Complications
Even with the most skilled practitioners, surgical complications can occur. One common issue is improper implant placement. If the implant is not positioned correctly, it may not integrate well with the bone. This misalignment can cause stress on the surrounding tissues and lead to failure.
Another surgical complication involves nerve damage. During the drilling process, if a nerve is accidentally damaged, it can lead to severe pain, numbness, or even the inability to use the affected area properly. This complication can require the removal of the implant and further surgical interventions.
Furthermore, inadequate surgical techniques can also be a culprit. The success of dental implants relies heavily on the surgical skills of the practitioner. Poor technique can result in insufficient initial stability of the implant, improper angulation, or insufficient depth, all contributing to potential implant rejection.
Material Incompatibility
The materials used in dental implants are typically biocompatible, but material incompatibility can still occur. Titanium and its alloys are commonly used due to their high success rate, but some patients may have allergic reactions or sensitivities to these materials. These adverse reactions can result in the body’s refusal to integrate the implant properly.
Another aspect of material incompatibility includes the quality of the implant materials. Lower-quality implants may lack the necessary durability and stability, leading to mechanical failures. It is crucial to use implants that have been tested and certified to meet industry standards.
Lastly, the presence of microscopic contaminants on the implant surface can also cause issues. Proper sterilization and handling procedures are essential to prevent contamination. Any foreign particles or residues can provoke an immune response, leading to implant rejection.
Understanding these factors can help both patients and dental professionals take the necessary steps to minimize the risk of implant rejection. For more detailed insights into dental implants and related topics, don’t hesitate to explore our other articles.
Prevention Strategies for Dental Implant Rejection
Dental implant rejection is an unfortunate outcome that can be distressing for both the patient and the clinician. To minimize the risk of rejection, it is imperative to follow a comprehensive and multifaceted approach. This includes a thorough examination during pre-surgical consultations, meticulous post-surgical care, and ongoing monitoring to ensure the longevity and success of the dental implant.
By adhering to evidence-based practices and employing the latest advancements in the field, dental professionals can significantly reduce the incidence of implant rejection. This article delves into effective prevention strategies that encompass pre-surgical consultations and post-surgical care, ensuring a holistic approach to implantology.
Pre-Surgical Consultations
Pre-surgical consultations are the cornerstone of a successful dental implant procedure. During this phase, a comprehensive assessment of the patient’s overall health, dental history, and specific needs is conducted. Medical history is critically important as conditions such as diabetes, osteoporosis, and smoking can adversely affect osseointegration. A detailed review helps in planning the procedure and foreseeing potential complications.
Radiographic imaging, including CBCT scans (Cone Beam Computed Tomography), plays a crucial role in evaluating the bone structure, identifying any anatomical challenges, and determining the optimal placement for the implant. This pre-surgical evaluation helps in formulating a customized treatment plan that maximizes the chances of success.
A proper oral hygiene assessment is also imperative. Patients must achieve a baseline of oral health by addressing any existing issues such as periodontal disease, cavities, or infections. This step ensures that the mouth is in the best condition possible to support the implant and promote healing.
Post-Surgical Care and Monitoring
Post-surgical care is integral to the overall success of a dental implant. Immediately after the surgery, patients should follow a strict post-operative regimen that includes taking prescribed antibiotics to prevent infection, using antiseptic mouthwash, and avoiding certain foods and activities that might disturb the implant site.
Regular follow-up appointments are essential for monitoring the healing process and early detection of potential issues. During these visits, radiographic evaluations and clinical examinations are performed to ensure that the implant is properly integrating with the bone. Any signs of complications, such as inflammation or infection, can be addressed promptly during these follow-ups.
Patient education is a key component of post-surgical care. Providing detailed instructions about oral hygiene practices and the importance of regular dental visits can significantly reduce the risk of implant rejection. Patients should be encouraged to maintain a healthy lifestyle, including quitting smoking and managing underlying health conditions, to support implant longevity.
In conclusion, preventing dental implant rejection involves a meticulous and multifaceted approach that starts with pre-surgical consultations and extends to diligent post-surgical care and monitoring. By adhering to these strategies, dental professionals can enhance the success rates of implants and improve patient outcomes. For more insights into advanced practices in implantology, explore other articles on our site.
Frequently Asked Questions About Dental Implant Rejection
If you are considering dental implants or have concerns about implant rejection, here are some common questions and straightforward answers to help clarify this issue.
What are the most common signs of dental implant rejection?
The most noticeable signs of dental implant rejection include pain, swelling, and inflammation at the implant site, which persist beyond the normal healing period. Other symptoms can include difficulty chewing and a feeling of looseness of the implant. If you experience these symptoms, it is crucial to consult with your dentist immediately.
How can I reduce my risk of dental implant rejection?
To minimize the risk of rejection, it’s important to maintain good oral hygiene, attend all follow-up appointments with your dentist, and ensure you do not smoke, as smoking can interfere with the healing process. Additionally, choosing an experienced implant dentist who can properly assess bone density and correctly place the implant is key to a successful outcome.

My name is Salman Kapa, a 73-year-old expert in bone regeneration and dental implantology. With decades of experience in the field, I am dedicated to advancing our understanding of oral health and hygiene. Through my research and writing, I aim to contribute to the development of innovative solutions in dental care.