Understanding the relationship between dental implants and gum disease is crucial for anyone considering this restorative treatment. While dental implants offer a permanent solution for missing teeth, their success largely depends on maintaining healthy gums and preventing periodontal disease. Regular dental check-ups, proper oral hygiene, and early intervention are essential factors that contribute to the longevity of dental implants and the prevention of gum-related complications.
Can implants cause gum problems?
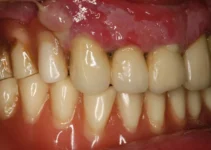
While dental implants are highly successful treatments for tooth replacement, they can potentially lead to gum-related complications if not properly maintained. The most significant concerns are peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis, which affect the soft and hard tissues surrounding dental implants. These conditions can develop due to bacterial accumulation, similar to natural teeth, but require specialized attention due to the unique interface between the implant and surrounding tissues.
Research indicates that approximately 20-30% of implant patients may experience some form of peri-implant disease during their lifetime. The key difference between implant-related gum issues and natural tooth problems lies in the absence of periodontal ligament around implants, making them more susceptible to rapid progression of infection once it starts.

Modern implant surfaces and connections have significantly improved tissue response and reduced complication rates. However, maintaining proper oral hygiene and regular professional monitoring remain crucial factors in preventing gum problems. The implementation of PRGF (Plasma Rich in Growth Factors) technology has shown promising results in improving soft tissue healing and reducing the risk of complications.
Early signs of implant-related gum issues
Recognizing early warning signs is crucial for preventing serious complications. The most common initial symptoms include:
- Redness and swelling around the implant
- Bleeding during brushing or spontaneous bleeding
- Increased sensitivity or discomfort
- Changes in gum color or texture
Professional monitoring should focus on detecting subtle changes in the peri-implant sulcus depth and evaluating the stability of surrounding soft tissues. Regular radiographic assessment can help identify early bone loss patterns before they become clinically evident. Patients should be educated about the importance of self-monitoring and reporting any changes in their implant sensation or appearance. Early intervention can often prevent the progression to more serious conditions and maintain long-term implant success.
Risk factors for implant complications
Several key factors can increase the likelihood of developing gum problems around dental implants. Smoking remains one of the most significant risk factors, with studies showing up to three times higher failure rates in smokers compared to non-smokers. Poor oral hygiene and pre-existing periodontal disease also significantly impact implant success rates.
Medical conditions that affect healing and immune response can compromise implant health:
- Uncontrolled diabetes
- Autoimmune disorders
- Osteoporosis
- Radiation therapy history
The quality and quantity of surrounding soft tissue play a crucial role in maintaining implant health. Insufficient keratinized tissue around implants can lead to increased susceptibility to bacterial invasion and tissue breakdown. Professional evaluation of tissue biotype and appropriate soft tissue management are essential components of successful implant therapy.
If you’re interested in learning more about dental implant care and maintenance, we encourage you to explore our other articles on advanced implant techniques and long-term success strategies. Understanding these aspects is crucial for achieving optimal results with your dental implants.
How does the immune system react with dental implants?
The interaction between dental implants and the human immune system represents a fascinating biological process that directly impacts treatment success. When a titanium implant is introduced into the jawbone, it triggers a complex cascade of immune responses that ultimately determine whether the implant will successfully integrate with the surrounding tissue.
Understanding this immune response is crucial for dental professionals, as it helps predict and manage potential complications. The body’s reaction to dental implants involves multiple immune system components, including macrophages, neutrophils, and various cytokines that work together to either accept or reject the foreign material.
Recent studies have shown that the surface properties of dental implants, particularly their microscopic texture and chemical composition, play a vital role in modulating the immune response. Modern implant surfaces are specifically designed to promote favorable immune reactions that support osseointegration while minimizing inflammatory responses.
Initial immune response to implants
Immediately following implant placement, the body initiates an acute inflammatory response as part of the natural healing process. This response is characterized by the rapid recruitment of neutrophils and macrophages to the implant site, which occurs within hours of the surgical procedure.
The initial phase involves the formation of a protein layer on the implant surface, known as the acquired pellicle. This process is crucial as it influences:
- Cell attachment and proliferation
- Immune cell recruitment and activation
- Formation of new blood vessels
- Initial bone healing response
During the first few days, the immune system orchestrates a careful balance between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory signals. This balance is essential for proper healing and determines the early success of the implant integration process.
Long-term immune adaptation
As the healing process progresses, the immune system transitions from an acute response to a more regulated, chronic state. The long-term success of dental implants largely depends on the body’s ability to maintain a state of controlled inflammation around the implant surface.
Research has identified several key factors that influence successful long-term immune adaptation:
- Proper maintenance of peri-implant tissue health
- Control of bacterial biofilm formation
- Patient’s overall immune system function
- Quality of the surrounding soft tissue barrier
The establishment of a healthy soft tissue seal around the implant is particularly crucial for long-term success. This biological seal helps prevent bacterial invasion and maintains a stable immune environment around the implant.
Modern implant technologies continue to evolve, incorporating features that promote positive immune responses and reduce the risk of complications. For more detailed information about specific implant maintenance techniques and the latest developments in implant technology, we encourage you to explore our other articles on dental implant care and innovation.
Main Problems That Dental Implants Can Cause in the Gums
Dental implants, while highly successful in restoring oral function and aesthetics, can sometimes lead to complications affecting gum health. The interface between the implant and surrounding gum tissue is crucial for long-term success. Understanding these potential issues is essential for both practitioners and patients to ensure proper maintenance and early intervention when necessary.
One of the most significant challenges is maintaining adequate keratinized gingival tissue around implants. Without sufficient gum tissue, implants become more susceptible to complications such as peri-implantitis and tissue recession. The BTI technique has revolutionized how we approach these challenges, offering solutions through careful tissue management and biological enhancement protocols.
The prosthetic-implant connection also plays a vital role in gum health. Bacterial microleakage at this interface can trigger inflammatory responses and tissue deterioration. Modern implant systems incorporate advanced sealing mechanisms to minimize these risks, but regular monitoring remains essential.
Common Gum Complications
Peri-implant diseases represent the most frequent complications affecting implant longevity. These conditions typically manifest in two main forms:
- Peri-implant mucositis: Reversible inflammation of soft tissues
- Peri-implantitis: Progressive bone loss around implants
- Gingival recession: Exposure of implant surfaces
- Tissue dehiscence: Gap formation in gum tissue
Clinical studies have shown that approximately 43% of implant patients may experience some form of peri-implant disease during their lifetime. Early detection through regular monitoring is crucial for successful intervention and treatment.
The impact of these complications can range from mild discomfort to significant tissue damage. Research indicates that patients with inadequate oral hygiene or a history of periodontal disease are at higher risk for developing complications.
Prevention and Treatment Strategies
Modern implant dentistry emphasizes preventive approaches to maintain optimal gum health. The implementation of professional cleaning protocols and regular monitoring helps identify potential issues before they become severe complications.
Advanced treatment options include:
- PRGF therapy for tissue regeneration
- Soft tissue grafting procedures
- Professional implant surface decontamination
- Antimicrobial protocols
The use of connective tissue grafts has shown remarkable success in addressing insufficient keratinized tissue around implants. Studies demonstrate that augmenting the gingival tissue can significantly improve long-term implant stability and aesthetic outcomes. To learn more about maintaining optimal oral health with dental implants, we encourage you to explore our other articles on advanced dental procedures and preventive care strategies. Understanding these aspects is crucial for achieving long-lasting success with your dental implants.
Understanding Dental Implant Success and Gum Health
When it comes to dental implants, maintaining healthy gums and proper hygiene is crucial for long-term success. Professional care and monitoring of gum tissue are essential factors that every patient should understand.