Understanding dental infections is crucial for maintaining oral health. These infections can originate from various sources such as tooth decay, gum disease, or after dental procedures. Recognizing the symptoms early, such as persistent toothache, sensitivity, swelling, or a foul taste, is key to preventing complications. It’s essential to consult a dentist for professional advice if symptoms persist or worsen to avoid potential severe health issues. Timely intervention by a dental professional can prevent the spread of infection and preserve your oral and overall health.
Common Symptoms of Dental Infections
Dental infections are a frequent concern for many patients and can lead to severe complications if not addressed promptly. Recognizing the common symptoms of dental infections is crucial for early intervention and effective treatment. Understanding these signs can also help in preventing further oral health issues.
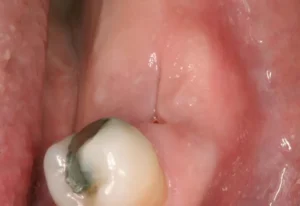
Dental infections often manifest through multiple symptoms that can vary in intensity. Some of these symptoms are quite pronounced and should be addressed immediately.  Here, we will discuss the most common symptoms, including persistent pain and swelling or redness of the gums.
Here, we will discuss the most common symptoms, including persistent pain and swelling or redness of the gums.
Persistent Pain
One of the most telling symptoms of a dental infection is persistent pain. This kind of pain is typically continuous and doesn’t subside with over-the-counter pain relievers. The pain might be localized to a specific tooth or can radiate through the jaw, indicating a more severe infection.
Persistent pain can arise from several dental issues, such as:
- Dental abscesses
- Severe tooth decay
- Gum disease
The pain is usually accompanied by other symptoms like sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures, making it difficult for the patient to eat or drink comfortably. If you experience such persistent pain, it’s essential to seek professional help immediately.
Swollen or Red Gums
Swollen or red gums are another common indicator of a dental infection. These symptoms often signal underlying issues like gingivitis or periodontitis, both of which can lead to more severe health problems if untreated. Swelling and redness in the gums can also cause discomfort and bleeding, especially while brushing or flossing.
Swollen or red gums typically suggest the presence of:
- Bacterial infection
- Accumulation of plaque or tartar
- Advanced gum disease
In some cases, the gums might feel tender to the touch or appear shiny due to the inflammation. Ignoring these symptoms can lead to the infection spreading to other parts of the mouth or even the jawbone.
Understanding and recognizing these symptoms can aid in prompt treatment, potentially avoiding complications that could arise from untreated dental infections. For further insights on dental health, explore our other articles on advanced dental care and preventive measures.
Types of Dental Infections
Dental infections can range from mild irritation to severe conditions that require immediate attention. These infections are predominantly caused by bacteria and can affect different parts of the mouth, including teeth, gums, and surrounding tissues. Understanding the various types of dental infections is crucial for timely treatment and effective management. Here, we will explore three common types: abscessed tooth, gingivitis, and periodontitis.
It’s essential to identify the symptoms early and seek professional dental care to prevent complications. Early intervention can save teeth and minimize the need for extensive dental procedures. Let’s delve into each type of dental infection to understand their causes, symptoms, and treatments better.
Abscessed Tooth
An abscessed tooth is a pocket of pus caused by a bacterial infection. This infection occurs in the tooth’s pulp, which contains blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissue. There are two main types of dental abscesses: periapical abscess, which occurs at the tip of the root, and periodontal abscess, which occurs in the gums next to a tooth root.
The primary symptoms of an abscessed tooth include severe, continuous, and throbbing pain in the affected tooth, sensitivity to hot and cold temperatures, fever, and swelling in the face or cheek. Pus drainage and bad taste in the mouth are also common. If not treated promptly, the infection can spread to other areas, leading to more severe health issues. Treatment options for an abscessed tooth often include antibiotics to treat the infection, drainage of the abscess, or a root canal procedure. In severe cases, the tooth may need to be extracted to stop the infection from spreading. Maintaining good oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups can help prevent the occurrence of abscessed teeth.
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is the mildest form of periodontal disease and is characterized by inflammation of the gums. It is primarily caused by plaque accumulation on the teeth, which harbors bacteria that irritate the gums. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to more severe forms of gum disease.
Common symptoms of gingivitis include red, swollen, and tender gums that bleed easily during brushing or flossing. Bad breath and a receding gum line are also indicators of this condition. Despite these noticeable symptoms, gingivitis is often painless, leading many individuals to overlook the early signs.
The key to treating gingivitis is improved oral hygiene. This includes brushing and flossing regularly to remove plaque, as well as professional dental cleanings to eliminate tartar build-up. Using an antiseptic mouthwash can also help reduce bacteria and inflammation. Early intervention is crucial to prevent the progression to periodontitis.
Periodontitis
Periodontitis is a severe gum infection that damages the soft tissue and destroys the bone that supports your teeth. It is a progression from untreated gingivitis and can lead to tooth loss if not managed appropriately. Periodontitis is associated with increased risks of systemic conditions, such as heart disease and diabetes.
Symptoms of periodontitis include swollen gums, bright red or purplish gums, and gums that feel tender when touched. Pus between the teeth and gums, bad breath, and loose teeth are also common signs. In advanced stages, the bone can become deteriorated, leading to tooth loss.
Treatment for periodontitis involves deep cleaning procedures like scaling and root planing, where the dentist removes plaque and tartar below the gum line and smooths the root surfaces. In severe cases, surgical interventions such as flap surgery or bone and tissue grafts may be necessary. Maintaining good oral hygiene and regular dental visits are critical in managing periodontitis effectively.
In conclusion, dental infections such as abscessed teeth, gingivitis, and periodontitis can have significant implications for oral and overall health. Recognizing the symptoms early and seeking professional dental care can prevent severe complications. To learn more about dental care and other related topics, don’t forget to check out our other informative articles.
When to Seek Professional Help
Oral health is a critical component of overall well-being. While minor issues such as a slight toothache or mild sensitivity can often be managed with home remedies, there are certain circumstances where seeking professional dental care becomes imperative. Delay in addressing severe symptoms can lead to more serious complications, underscoring the importance of timely intervention.
Recognizing the signs that warrant professional help can save you from long-term dental issues and even protect your overall health. Whether it’s a relentless toothache, unexpected swelling, or difficulty swallowing, knowing when to contact your dentist is crucial. Below, we explore the specific situations where professional dental care should be sought without delay.
Severe Pain
Experiencing severe pain in your teeth or gums is a clear signal that you need to seek professional dental help. This type of pain is often indicative of underlying issues such as an abscessed tooth, advanced decay, or a fractured tooth. Ignoring severe pain can lead to more complicated problems, including infections that may spread to other parts of your body. Signs that your pain may be severe include:
- Pain that is persistent and does not go away with over-the-counter pain relievers.
- Pain that is accompanied by swelling or redness in the gums.
- Sharp or throbbing pain that keeps you awake at night.
If you experience any of the above symptoms, contact your dentist immediately for a thorough examination and appropriate treatment. Ignoring these signs can lead to increased damage and the need for more invasive procedures down the line.
Fever and Swelling
The presence of a fever and swelling in your mouth or face can be indicative of a serious infection. These symptoms often signal an abscess, which is a pocket of pus caused by a bacterial infection. An abscessed tooth or gum infection can escalate quickly and may even affect your general health if not treated promptly.
Key indicators that an infection is serious include:
- Swelling that persists and is noticeably increasing.
- A consistent fever that does not subside with antipyretics.
- A foul taste in the mouth or difficulty in opening your mouth.
It is crucial to seek dental care immediately if you exhibit these symptoms. Delaying treatment for infections can lead to complications such as the infection spreading to other tissues, or even systemic issues like sepsis.
Difficulty Eating or Swallowing
Experiencing difficulty when eating or swallowing is another red flag that you should consult with your dentist. This discomfort can be caused by a variety of serious conditions including advanced tooth decay, gum disease, or even oral cancer. Identifying the root cause is crucial to proper treatment.
Signs that point to the need for professional attention include:
- Persistent pain or discomfort when chewing or swallowing.
- Feeling of something being stuck in your throat.
- Unexplained weight loss due to difficulty in eating.
Ignoring these symptoms can severely affect your nutrition and overall health, leading to more severe health issues over time. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent further complications and ensure that you remain in good health.
In conclusion, when it comes to your oral health, it’s always better to be proactive rather than reactive. If you’re experiencing any of the symptoms mentioned, it’s crucial to seek professional advice immediately. For more tips and information on maintaining optimal oral health, be sure to check out our other articles.
Identifying and Managing Dental Infections
Understanding how to recognize and respond to dental infections is crucial for maintaining oral health. Here are some common questions and answers to help you detect signs of infection and decide when to consult a dental professional.
What are the typical signs of a dental infection?
Symptoms of a dental infection can vary, but common signs include persistent toothache, swelling in the gums or face, sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures, bad breath, a foul taste in the mouth, and fever. If the infection is severe, swelling can extend to the jaw, neck, or floor of the mouth, which can be a medical emergency. Recognizing these symptoms early is key to effective treatment.
When should I seek professional help for a dental infection?
You should consult a dentist if you experience any symptoms of dental infection, especially if the pain is persistent, severe, or associated with swelling or fever. Early professional intervention can prevent the spread of the infection and more complicated health issues. In cases of severe swelling, difficulty breathing or swallowing, or fever, immediate medical attention is necessary as these symptoms can indicate a more serious condition.

My name is Salman Kapa, a 73-year-old expert in bone regeneration and dental implantology. With decades of experience in the field, I am dedicated to advancing our understanding of oral health and hygiene. Through my research and writing, I aim to contribute to the development of innovative solutions in dental care.