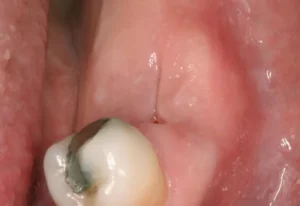
A gum abscess, frequently referred to as a periodontal abscess, is a painful condition that occurs when a pus-filled pocket forms in the gum due to an infection. It is often caused by severe gum disease (periodontitis), food trapped between the tooth and gum, or a combination of both. Identifying the symptoms early is crucial for effective treatment and may include severe discomfort, red and swollen gums, or a bad taste in the mouth. Proper dental hygiene and regular dental visits are essential for prevention and early detection.
Causes of Gum Abscess
A gum abscess, also known as a periodontal abscess, is a painful condition that occurs when pus builds up in the tissue surrounding a tooth. This condition is primarily caused by an infection, but there are several underlying factors that can contribute to its development. Understanding the causes of gum abscess is crucial for prevention and effective treatment. Here, we will explore two major causes: bacterial infection and poor oral hygiene.
Gum abscesses can escalate quickly and lead to severe discomfort if left untreated. Knowing what triggers this condition can help in taking proactive measures to maintain oral health. Let’s delve into the primary causes in more detail.
Bacterial Infection
The most common cause of a gum abscess is a bacterial infection. When bacteria enter the gum tissue through a break or tear, they can proliferate and lead to an abscess. These bacteria usually originate from plaque, the sticky film that forms on teeth. The bacteria in plaque produce toxins that irritate the gums, causing inflammation and an immune response from the body. This immune response often results in the formation of pus.
Specific bacteria, such as Streptococcus and anaerobic bacteria, are often implicated in gum abscesses. These organisms thrive in environments that lack oxygen, such as periodontal pockets. Periodontal pockets are spaces that form when the gums pull away from the teeth, creating a breeding ground for harmful bacteria.
It is also important to note that untreated gum disease, also known as periodontitis, can lead to abscess formation. Periodontitis destroys the supporting structures of the teeth, making it easier for bacteria to invade and cause an abscess. Early intervention and treatment of bacterial infections can significantly reduce the risk of developing a gum abscess.
Poor Oral Hygiene
Poor oral hygiene is another significant factor that can lead to a gum abscess. When proper oral care routines are neglected, plaque can accumulate on the teeth and gums. Accumulated plaque increases the risk of gum disease, which in turn can lead to abscess formation. Daily brushing and flossing are essential practices to remove plaque and prevent bacterial proliferation.
Furthermore, poor oral hygiene can result in the formation of dental caries, or cavities, which are essentially holes in the teeth caused by bacterial activity. These cavities can become infected and lead to abscesses if not treated promptly. Regular dental check-ups are crucial for identifying and addressing such issues before they escalate into more serious conditions.
In addition to basic oral care, lifestyle habits such as smoking and a poor diet can exacerbate oral health issues. Smoking, in particular, is known to impair the immune system’s ability to fight off infections, making smokers more susceptible to gum abscesses. A diet high in sugar and carbohydrates can also promote the growth of harmful bacteria in the mouth.
Maintaining good oral hygiene and adopting healthy lifestyle habits can significantly lower the risk of developing a gum abscess. By being proactive and diligent about oral care, individuals can protect themselves from this painful and potentially serious condition.
To gain a deeper understanding of oral health, consider exploring our other articles. They provide valuable insights into various dental conditions and tips for maintaining a healthy smile.
Symptoms of Gum Abscess
A gum abscess, also known as a dental abscess, is a localized infection in the gum tissue that can cause significant discomfort and other severe symptoms. Recognizing the symptoms early can help in seeking timely treatment, thus preventing further complications. Common symptoms of a gum abscess include severe pain, swelling, and a foul taste in the mouth. Each of these symptoms is a clear indicator that something is amiss and requires professional dental evaluation.
It’s crucial to understand the severity of these symptoms, as they can impact your overall oral health and potentially lead to more serious issues if left untreated. Immediate attention and proper management are essential to alleviate the discomfort and resolve the infection effectively. Let’s examine each symptom more closely to better understand how they present and what they signify.
Severe Pain
One of the most prominent symptoms of a gum abscess is severe pain. This pain is typically localized to the area of the infection but can radiate to other parts of the face, neck, or even the ear. The pain is often described as a throbbing or pulsating sensation that can be persistent and debilitating. This is usually due to the pressure buildup from the accumulation of pus in the infected area. The intensity of the pain can increase with activities such as chewing, biting, or even brushing your teeth. It can also be more pronounced when lying down, as the blood pressure in the head increases, exacerbating the discomfort.
Ignoring this symptom can lead to more severe complications. If the infection spreads, it can affect surrounding tissues and bones, leading to a condition known as cellulitis, or even more severe systemic infections that can be life-threatening in rare cases.
Swelling
Swelling is another key symptom of a gum abscess. The infected area often becomes visibly swollen as your body responds to the infection by sending immune cells to the site. This swelling can cause the affected gum to appear red and puffy and may extend to the surrounding areas, including the face and neck.
In more severe cases, the swelling can cause noticeable asymmetry in the face, leading to significant discomfort and difficulty with daily activities such as speaking and eating. This swelling is a result of the immune response to the infection and the accumulation of toxins and debris at the site.
If left untreated, the swelling can compromise the airways and other critical structures, presenting a more significant health risk. Early intervention is crucial to manage the infection and reduce the inflammatory response effectively.
Foul Taste in Mouth
A foul taste in the mouth is another common symptom of a gum abscess. This unpleasant taste is often due to the draining of pus from the infection site into the mouth. Pus contains dead tissue, bacteria, and immune cells, which contribute to the foul odor and taste. This symptom is usually most noticeable when the abscess has ruptured.
In addition to the bad taste, this can also lead to bad breath, which can be socially distressing. Regular oral hygiene practices may not alleviate this symptom, and it often persists until the underlying infection is treated.
The presence of a foul taste or bad breath, along with other symptoms like pain and swelling, should prompt immediate dental consultation. Addressing the infection not only resolves the unpleasant taste and odor but also prevents further oral health complications.
Understanding the symptoms of a gum abscess is the first step toward seeking effective treatment. For more insights into dental health and preventive care, be sure to explore our other articles. Stay informed to keep your smile healthy and bright!
Diagnosis and Treatment
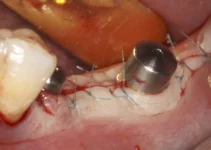
The diagnosis and treatment of dental issues, particularly those requiring implantology and bone regeneration, involve a meticulous process. An accurate diagnosis is the cornerstone of successful treatment, which ensures that the underlying causes of dental problems are addressed effectively. The process typically encompasses a series of steps that include clinical examination, imaging techniques such as X-rays, and, if necessary, procedures to manage immediate concerns such as abscesses.
Advancements in dental technology have significantly enhanced the precision of diagnoses and the effectiveness of treatments. Understanding the specific methodologies used in these processes is crucial for both patients and practitioners. This section delves into the essential components of diagnosis and treatment in the field of implantology and bone regeneration.
Clinical Examination
A thorough clinical examination is the first step in diagnosing dental issues. This involves a detailed assessment of the patient’s oral cavity, including the teeth, gums, and surrounding tissues. Dentists look for signs of inflammation, infection, or other abnormalities that could indicate underlying problems. The examination also includes a review of the patient’s dental and medical history, which can provide valuable context for current issues.
During the clinical examination, several diagnostic tools may be used, such as periodontal probes, which measure the depth of gum pockets, and exploratory instruments to detect cavities and other defects. Additionally, dentists may perform palpation techniques to feel for any irregularities or swelling in the jaw and neck regions. Key aspects often evaluated during a clinical examination include:
- Gum health: Inspecting for signs of gum disease, such as redness, swelling, or bleeding.
- Tooth integrity: Checking for decay, cracks, or damage.
- Occlusion: Assessing the alignment and bite of the teeth.
Clinical examination lays the groundwork for further diagnostic procedures, ensuring that a comprehensive understanding of the patient’s condition is obtained.
X-rays
X-rays play a pivotal role in dental diagnosis as they offer a detailed view of the teeth, bones, and surrounding structures. These imaging techniques are indispensable in identifying issues that are not visible during a clinical examination. Dental X-rays can reveal problems such as bone loss, infections, and impacted teeth.
There are several types of dental X-rays, each serving a specific purpose:
- Bitewing X-rays: Commonly used to detect decay between teeth.
- Periapical X-rays: Provide a complete view of a single tooth, from the crown to the root.
- Panoramic X-rays: Capture the entire mouth in one image, useful for planning implants and detecting complex issues.
The information gleaned from X-rays allows dentists to plan appropriate treatments with greater accuracy. For example, in the context of implantology, X-rays help determine the quality and quantity of the bone, which is critical for successful implant placement.
Furthermore, advancements in digital radiography have reduced radiation exposure and improved image quality, making X-rays a safer and more effective diagnostic tool.
Drainage of Abscess
A dental abscess is a pocket of pus caused by a bacterial infection. Addressing an abscess promptly is crucial to prevent the spread of infection and alleviate pain. The drainage of an abscess is often an immediate concern in dental treatment and can be a precursor to other procedures such as implantology.
The procedure for draining an abscess typically involves the following steps:
- Administering a local anesthetic to numb the area.
- Making a small incision in the gum to allow the pus to drain out.
- Cleaning the abscessed area thoroughly to remove any remaining infection.
- Prescribing antibiotics to eliminate the bacterial infection and prevent recurrence.
After drainage, a follow-up examination ensures that the infection is under control. In the context of implantology and bone regeneration, ensuring that the patient is free of infections is essential before proceeding with further treatments.
In summary, the diagnosis and treatment of dental issues require a combination of clinical examination, imaging techniques, and immediate interventions like abscess drainage. Accurate and comprehensive diagnosis sets the stage for effective treatment, ensuring optimal outcomes for implantology and bone regeneration.
For more detailed information on other aspects of dental care, including advanced implantology techniques and bone regeneration strategies, be sure to explore our other articles.
Treatment and Prevention of Gum Abscesses
Understanding how to treat and prevent gum abscesses is crucial for maintaining oral health and avoiding more serious complications. Here are some common inquiries regarding the management and prevention strategies.
What are the treatment options for a gum abscess?
The treatment for a gum abscess typically involves draining the abscess to eliminate infection, followed by a thorough cleaning of the affected area. Depending on the severity, antibiotics may be prescribed to help fight the infection. In cases where the abscess is caused by gum disease or a decayed tooth, further treatments such as scaling and root planing, root canal therapy, or even tooth extraction might be necessary.
How can gum abscesses be prevented?
Preventing gum abscesses starts with good oral hygiene practices including regular brushing, flossing, and using mouthwash. It’s also important to maintain regular dental check-ups and cleanings. Avoiding smoking and maintaining a healthy diet contribute to healthier gums. If early signs of gum disease are detected, such as swelling or bleeding gums, it’s crucial to seek dental advice promptly to prevent the development of abscesses.

My name is Salman Kapa, a 73-year-old expert in bone regeneration and dental implantology. With decades of experience in the field, I am dedicated to advancing our understanding of oral health and hygiene. Through my research and writing, I aim to contribute to the development of innovative solutions in dental care.