Understanding how diabetes impacts oral health is crucial for maintaining both dental and overall wellness. When blood sugar levels are not properly managed, individuals with diabetes are at a higher risk for numerous dental problems, including gum disease, dry mouth, and slower healing after dental procedures. Elevated glucose levels in saliva can promote the growth and accumulation of harmful bacteria, leading to increased plaque and tartar build-up. These conditions not only worsen gum disease but can also lead to more severe infections and tooth loss if not addressed promptly. Regular dental check-ups, proper hygiene practices, and effective diabetes management are essential components in preventing these adverse effects on dental health.
The Connection Between Diabetes and Oral Health
Diabetes is a chronic condition that impacts how the body processes blood sugar. It is well-known that those with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing various health issues, and oral health is no exception. Recent studies have shown a strong correlation between diabetes and increased susceptibility to gum diseases and other oral problems. Understanding these connections is key to managing both diabetes and oral health effectively.
Individuals with diabetes are more likely to experience oral health issues due to high blood sugar levels, which can affect the body’s healing processes and its ability to fight infections. Taking good care of your oral hygiene is essential for diabetics to prevent complications. Let’s delve deeper into the specific oral health problems that are commonly associated with diabetes.
From increased risks of gum disease to delayed healing, and dry mouth, the complications arising from diabetes can be numerous and varied. Understanding these issues in depth can help in taking proactive steps to manage them better. Here’s a closer look at the primary oral health concerns for diabetics.
Increased Risk of Gum Disease
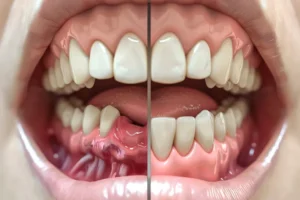
One of the most significant oral health risks for those with diabetes is an increased susceptibility to gum disease, also known as periodontal disease. Elevated blood sugar levels can lead to higher glucose levels in saliva, which promotes the growth of harmful bacteria in the mouth. This bacterial growth can cause the gums to become inflamed, leading to gingivitis and eventually periodontitis if left untreated. Studies have found that people with diabetes are up to three times more likely to develop periodontitis compared to those without the condition. Poorly controlled diabetes can exacerbate the inflammation and infection in the gums, further complicating oral health.
Prevention strategies for gum disease in diabetics include meticulous oral hygiene routines, regular dental check-ups, and managing blood sugar levels effectively. Dentists can also recommend specific treatments tailored for diabetic patients to prevent or mitigate gum disease.
Delayed Healing
Diabetes can significantly affect the body’s healing processes, including within the mouth. The condition can impair blood circulation, reduce the delivery of essential nutrients, and decrease the ability of the body’s cells to repair themselves. This delayed healing can make diabetics more vulnerable to infections and complications after dental procedures.
For instance, procedures such as tooth extractions or dental implants may take longer to heal in diabetic patients. This delay can lead to an increased risk of infections and other oral health problems. It’s crucial for diabetics to inform their dentist about their condition to tailor the care plan accordingly.
Effective blood sugar management plays a vital role in promoting faster healing and reducing the risk of complications. Maintaining good oral hygiene and following the dentist’s post-procedure recommendations are also essential for promoting healing.
Dry Mouth and Its Effects
Dry mouth, or xerostomia, is another common issue faced by those with diabetes. High blood sugar levels can cause reduced saliva production, which leads to dry mouth. Saliva is essential for washing away food particles and neutralizing acids in the mouth, helping to prevent tooth decay and gum disease.
Without adequate saliva, diabetics can experience a higher incidence of cavities, sore mouth, infections, and difficulties in chewing and swallowing. Dry mouth also makes it easier for bacteria to thrive, contributing further to oral health issues.
Managing dry mouth involves staying hydrated, using saliva substitutes or mouthwashes specifically designed for dry mouth, and regularly chewing sugar-free gum to stimulate saliva production. It’s also crucial to maintain stringent oral hygiene practices to counteract the effects of dry mouth.
The intricate relationship between diabetes and oral health underscores the importance of comprehensive care routines and regular dental visits. Understanding these connections can enable diabetics to take proactive steps to protect their oral health. For more detailed information on managing oral health issues related to diabetes, consider reading other articles on our website.
Common Dental Problems in Diabetic Patients
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels. This imbalance can lead to various health complications, including those related to oral health. Diabetic patients are more susceptible to dental issues due to their compromised immune system and reduced healing capabilities. Consequently, maintaining good oral hygiene and regularly visiting a dentist are crucial for managing diabetes and preventing dental problems.
Several dental problems are commonly observed in diabetic patients. Understanding these issues can help in early detection and treatment, ensuring that complications are minimized. In this article, we will explore some of the most prevalent dental problems faced by individuals with diabetes: Periodontitis, Tooth Decay, and Oral Thrush.
Periodontitis
Periodontitis, also known as gum disease, is a severe infection of the gums that can destroy the bone supporting the teeth if left untreated. Diabetic patients are at a higher risk for periodontitis due to their reduced ability to fight bacterial infections. Elevated blood sugar levels can also promote the growth of bacteria in the mouth, further exacerbating the condition.
One of the key symptoms of periodontitis is persistent bad breath, swollen or bleeding gums, and loose teeth. It’s important for diabetic patients to manage their blood sugar levels effectively to reduce the risk of developing periodontitis. Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings can also help in early detection and management of the disease.
To manage periodontitis in diabetic patients, dentists may recommend a combination of treatments, including:
- Scaling and root planing (deep cleaning)
- Antibiotic therapy
- Periodontal surgery in severe cases
Tooth Decay
Tooth decay, or dental caries, is another common problem faced by diabetic individuals. High blood sugar levels can increase the amount of sugar in the saliva, promoting the growth of acid-producing bacteria that lead to cavities. Moreover, diabetic patients often experience dry mouth, a condition known as xerostomia, which can further contribute to tooth decay. The symptoms of tooth decay include toothache, sensitivity to hot or cold foods, and visible holes or pits in the teeth. Preventive measures such as maintaining good oral hygiene, using fluoride toothpaste, and reducing sugar intake can help mitigate the risk of tooth decay in diabetic patients.
Regular dental visits are essential for early detection and treatment of tooth decay. Dentists may recommend:
- Fluoride treatments
- Dental sealants
- Restorative procedures like fillings and crowns
Oral Thrush
Oral thrush, also known as oropharyngeal candidiasis, is a fungal infection caused by the overgrowth of Candida albicans in the mouth. Diabetic patients are more susceptible to this infection due to their weakened immune system and higher blood sugar levels, which provide a conducive environment for the fungus to thrive.
The symptoms of oral thrush include white patches on the tongue and inner cheeks, redness or soreness, and difficulty swallowing. Proper oral hygiene and managing blood sugar levels are crucial in preventing the onset of oral thrush. Antifungal medications are typically prescribed to treat the condition.
To prevent oral thrush, diabetic patients should:
- Practice good oral hygiene, including brushing and flossing daily
- Rinse their mouth after using inhalers
- Maintain well-controlled blood glucose levels
In conclusion, diabetes can significantly impact oral health, making individuals more vulnerable to conditions like periodontitis, tooth decay, and oral thrush. By understanding these risks and taking proactive measures, diabetic patients can better manage their oral health and overall well-being. For more information on diabetes and dental health, be sure to read our other articles.
Managing Oral Health with Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the body’s ability to process blood sugar. For individuals with diabetes, maintaining good oral health is especially important, given the higher risk of developing complications such as gum disease, tooth decay, and other oral infections. Monitoring and managing oral health can significantly improve overall health outcomes for diabetic patients.
Studies have shown that severe gum disease can increase blood sugar levels, complicating the management of diabetes. This bidirectional relationship means that effective oral care can help manage diabetes and vice versa. Therefore, integrating regular dental care into a diabetes management plan is crucial.
Regular Dental Checkups
One of the most critical aspects of managing oral health with diabetes is attending regular dental checkups. These visits allow for early detection of potential issues and prompt treatment, reducing the risk of severe complications. Dentists can provide tailored advice and treatments to help mitigate the effects of diabetes on oral health.
During these checkups, dentists often:
- Perform professional cleanings to remove plaque and tartar buildup
- Check for early signs of gum disease or tooth decay
- Monitor for any changes or complications related to diabetes
While a standard recommendation is to visit the dentist twice a year, individuals with diabetes might benefit from more frequent visits based on their specific needs and conditions.
Furthermore, regular dental checkups provide an opportunity for dentists to reinforce the importance of maintaining good oral hygiene practices and managing blood sugar levels effectively. They can also coordinate care with other healthcare providers to ensure a comprehensive approach to diabetes management.
Proper Oral Hygiene Practices
In addition to regular dental checkups, practicing proper oral hygiene at home is vital for individuals with diabetes. Effective daily oral care can greatly reduce the risk of gum disease and other oral health issues. Key practices include:
- Brushing teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste
- Flossing daily to remove plaque from between the teeth and gumline
- Using an antiseptic mouthwash to kill bacteria and freshen breath
It is also important for diabetic patients to monitor for signs of gum disease, which may include redness, swelling, and bleeding gums, as these can indicate the need for prompt dental care. Maintaining good oral hygiene can also help improve blood sugar control, creating a mutually beneficial cycle of health management.
Lastly, individuals should be mindful of their diet, as consuming excessive sugars and carbohydrates can exacerbate both oral health issues and diabetes complications. Staying hydrated, using xylitol-based products, and avoiding tobacco use are additional practices that can support better oral health outcomes.
For more detailed information and tips, consider exploring our other articles related to oral health and diabetes management.
Understanding Diabetes Impact on Oral Health
Diabetes is not only a systemic condition affecting blood sugar levels but also has significant impacts on dental health. Below are common inquiries about how this chronic ailment affects your teeth and gums.
How does diabetes influence oral health?
Diabetes primarily affects oral health by increasing the risk of gum disease, which can range from gum inflammation (gingivitis) to more severe infections and bone destruction (periodontitis). High blood sugar levels create an environment that fosters the growth of bacteria causing gum disease. Additionally, diabetes can lead to dry mouth due to decreased saliva production, which further increases the risk of tooth decay and other oral infections.
Are there specific oral health symptoms diabetics should watch for?
Yes, individuals with diabetes should be vigilant for symptoms such as bleeding gums, persistent bad breath, dry mouth, loose teeth, receding gums, and frequent oral infections. Early detection and management of these symptoms, together with controlling blood sugar levels, are crucial for maintaining good oral health and preventing more severe complications.

My name is Salman Kapa, a 73-year-old expert in bone regeneration and dental implantology. With decades of experience in the field, I am dedicated to advancing our understanding of oral health and hygiene. Through my research and writing, I aim to contribute to the development of innovative solutions in dental care.