Understanding how celiac disease influences oral health is crucial for maintaining overall wellbeing. Individuals with celiac disease often face various dental issues, such as enamel defects, recurring mouth ulcers, and delayed dental development. These symptoms can often be the first signs of the disease. Education about the interplay between celiac disease and oral health can lead to better preventative measures and treatment plans, enhancing the quality of life for those affected.
Introduction to Celiac Disease and Oral Health
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. When individuals with celiac disease consume gluten, their immune system responds by damaging the small intestine. This condition can lead to a variety of health issues, including nutritional deficiencies and complications in various bodily systems. One area of the body that can be particularly affected is the oral cavity.
In this article, we will explore the intricate relationship between celiac disease and oral health. Understanding how these two are interconnected can help in early diagnosis and management of both conditions. We will delve into the fundamentals of celiac disease, its symptoms, and provide an overview of its impact on oral health.
By acknowledging the link between celiac disease and oral health, dentists and healthcare providers can offer more comprehensive care. This awareness also empowers patients to take control of their health by recognizing early signs and seeking appropriate treatment.
Understanding Celiac Disease
Celiac disease is characterized by an adverse immune reaction to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. When people with this condition consume gluten, their immune system attacks the lining of the small intestine, leading to villous atrophy. This damages the villi, small finger-like projections that aid in nutrient absorption.
One of the key challenges in managing celiac disease is that its symptoms can vary widely and often mimic other conditions. These symptoms can range from gastrointestinal issues to neurological and even dermatological problems. Because of this, celiac disease is often underdiagnosed or misdiagnosed. Research indicates that both genetic and environmental factors play a role in the development of celiac disease. The presence of specific genes, like HLA-DQ2 and HLA-DQ8, increases an individual’s susceptibility to the disease. However, not everyone with these genetic markers will develop celiac disease, indicating the importance of environmental triggers such as infections or dietary patterns.
Symptoms of Celiac Disease
The symptoms of celiac disease can be diverse and affect multiple systems. Some of the most common gastrointestinal symptoms include:
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal pain
- Bloating and gas
- Weight loss
Non-gastrointestinal symptoms can also be prevalent, especially in children. These may include:
- Delayed growth and puberty
- Neurological symptoms such as headaches or numbness
- Arthritis or joint pain
- Dermatitis herpetiformis, a skin rash associated with celiac
Because the symptoms are so varied, diagnosing celiac disease often requires a combination of serological tests and biopsy of the small intestine. The presence of antibodies such as anti-tissue transglutaminase (tTG) and anti-endomysial antibodies (EMA) can support the diagnosis.
Overview of Oral Health
Oral health is an essential component of overall health and well-being. It involves the proper functioning and aesthetic appearance of the mouth, teeth, and gums. Maintaining good oral health is crucial as it is linked to multiple systemic conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and respiratory illnesses.
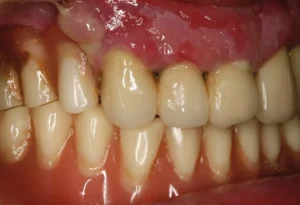
For individuals with celiac disease, oral health takes on added significance. Studies have shown that they are more prone to certain oral conditions, which can be crucial indicators of undiagnosed celiac disease. These conditions include:
- Dental enamel defects
- Recurrent aphthous stomatitis (canker sores)
- Atrophic glossitis (a smooth, red, and swollen tongue)
- Delayed dental development in children
Recognizing these oral manifestations can lead to earlier diagnosis and treatment of celiac disease. Regular dental check-ups and inter-professional communication between dentists and healthcare providers can facilitate better care for patients with celiac disease.
In conclusion, understanding the relationship between celiac disease and oral health can lead to better management and improved quality of life for affected individuals. Explore our other articles for more insights into how various systemic conditions can impact oral health and what you can do to maintain it.
Correlation Between Celiac Disease and Dental Problems
There is a significant body of evidence indicating a correlation between celiac disease and various dental problems. Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder where the ingestion of gluten leads to damage in the small intestine. This not only affects nutrient absorption but also has a variety of secondary effects on different aspects of health, including oral health. Research has consistently shown that people with celiac disease are more likely to suffer from dental enamel defects, recurrent aphthous stomatitis, and other oral health issues.
Among the dental problems frequently noted in celiac patients, dental enamel defects are particularly widespread. These defects can present as discoloration, pitting, or grooving of the teeth and are often symmetrical. Studies have shown that up to 96% of children with celiac disease exhibit some form of enamel defect. These dental manifestations usually occur symmetrically and are most commonly observed in the permanent teeth. The development of enamel hypoplasia in celiac disease patients is often attributed to the malabsorption of essential nutrients, such as calcium and vitamin D, which are crucial for proper enamel formation.
Another common oral health issue observed in individuals with celiac disease is recurrent aphthous stomatitis (RAS), also known as canker sores. These painful sores can significantly affect the quality of life and are thought to be related to the overall immune response in celiac disease. Additionally, the chronic malabsorption issues seen in celiac patients often lead to deficiencies in B vitamins, iron, and folic acid, which further contribute to the occurrence and severity of RAS. Studies suggest that addressing these nutritional deficiencies can help in alleviating the frequency and severity of canker sores.
Common Oral Manifestations of Celiac Disease
Celiac disease, an autoimmune disorder triggered by the ingestion of gluten, not only affects the small intestine but can also have significant oral manifestations. These oral symptoms can be an important clue for early diagnosis and management of the disease. Below are some of the common oral manifestations observed in patients with celiac disease.
Understanding these oral signs is crucial for dental professionals as they may be the first to detect indicators of the disease, facilitating quicker diagnosis and treatment. Recognizing these oral manifestations can also help in the multidisciplinary management of celiac disease, ensuring comprehensive patient care.
Dental Enamel Defects
One of the most common oral manifestations of celiac disease is dental enamel defects. These defects often appear as symmetric spots on the enamel of permanent teeth. Studies have shown that up to 95% of individuals with celiac disease have some form of enamel defect. These defects can present as:
- White, yellow, or brown spots
- Horizontal grooves
- Pitting of the teeth surface
Dentists should be aware that these enamel defects are usually bilaterally symmetrical and tend to occur on the incisors and molars. The presence of such defects may warrant further investigation into the patient’s diet and gastrointestinal health, potentially leading to the diagnosis of celiac disease.
Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis
Recurrent aphthous stomatitis (RAS), commonly known as canker sores, is another oral manifestation frequently observed in individuals with celiac disease. These painful, recurring ulcers can significantly impact the quality of life due to discomfort and difficulty in eating and speaking. The ulcers typically present as:
- Small, round or oval sores
- White or yellow centers with a red border
- Occurring on the inner cheeks, lips, tongue, or floor of the mouth
The exact cause of RAS in celiac disease is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to the immune response and nutritional deficiencies associated with malabsorption. Dentists should consider celiac disease as a differential diagnosis in patients with frequent and severe episodes of RAS.
Atrophic Glossitis
Atrophic glossitis, also known as smooth tongue, is characterized by a loss of papillae on the tongue’s surface, leading to a shiny, red appearance. This condition is often associated with nutritional deficiencies, which are common in celiac disease due to malabsorption. Symptoms of atrophic glossitis include:
- Burning sensation in the tongue
- Red, shiny tongue surface
- Sensitivity to certain foods
Patients with celiac disease may experience atrophic glossitis due to deficiencies in iron, folic acid, and vitamin B12. Addressing these nutritional deficiencies through diet modifications and supplements can help in managing this condition. It is essential for dental professionals to collaborate with healthcare providers to ensure a holistic approach to patient care.
Understanding these oral manifestations of celiac disease can significantly enhance the early detection and management of the condition. For more in-depth information on related topics, explore our other articles on oral health and systemic diseases.
Management and Prevention Strategies
Management and prevention of dental issues, particularly those that involve implantology and bone regeneration, require a strategic and multifaceted approach. By embracing a combination of healthy lifestyle choices and professional dental care, patients can significantly improve the longevity and success of their dental implants. This section explores several key strategies that can help maintain optimal oral health.
Developing an understanding of the relationship between systemic health and oral health is crucial for effective management and prevention. For instance, studies have shown that maintaining a balanced diet, practicing good oral hygiene, and having regular dental checkups are essential for preventing complications like peri-implantitis and ensuring successful implant outcomes. Below, we delve into some of these critical strategies in detail.
Adopting a Gluten-Free Diet
Emerging research suggests that adopting a gluten-free diet can have positive implications for oral health, particularly for individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity. These conditions can lead to malabsorption of essential nutrients such as calcium and Vitamin D, which are vital for bone health. By eliminating gluten from their diet, patients may enhance nutrient absorption and improve bone density, which is critical for the success of dental implants. Furthermore, a gluten-free diet can reduce inflammation in the body, including the gums. Chronic inflammation is a well-known contributor to periodontal diseases, which can jeopardize the stability of dental implants. Therefore, patients with gluten sensitivities might notice significant oral health improvements by adhering to a gluten-free regimen.
Incorporating a gluten-free diet involves:
- Eliminating wheat, barley, and rye from meals.
- Incorporating gluten-free grains such as rice and quinoa.
- Reading labels carefully to avoid cross-contamination.
Consistently following a gluten-free diet can lead to systemic and oral health benefits, thereby enhancing the outcomes of dental treatments, including implants.
Regular Dental Checkups
Regular dental checkups are a cornerstone of maintaining excellent oral health and ensuring the longevity of dental implants. Professional examinations enable early detection of potential issues such as peri-implantitis, which can compromise the success of an implant if left untreated. Dental practitioners can also provide tailored advice on maintaining oral hygiene and address any concerns patients may have regarding their implants.
During checkups, dental professionals can perform professional cleanings, removing plaque and tartar buildup that patients may miss with at-home care. This is particularly important for implant care, as build-up can lead to inflammation and infection around the implant site.
The American Dental Association recommends that individuals, especially those with dental implants, schedule checkups at least twice a year. These visits allow for:
- Comprehensive assessment of oral health.
- Professional cleanings.
- Early detection and intervention of potential issues.
By adhering to regular dental checkups, patients can proactively manage their oral health, ensuring the durability and success of their dental implants.
Oral Hygiene Practices
Effective oral hygiene practices are essential in preventing dental diseases and ensuring the long-term success of dental implants. A robust oral hygiene routine helps eliminate bacteria and plaque that can cause gum disease and peri-implantitis, thereby protecting the investment in dental implants.
A comprehensive oral hygiene regimen should include:
- Brushing twice daily with a soft-bristled toothbrush to avoid damaging the gums and implant surfaces.
- Flossing daily to remove food particles and plaque from areas that brushing alone cannot reach.
- Using an antimicrobial mouthwash to reduce bacterial load and maintain a healthy oral environment.
Patients should also consider the use of interdental brushes and water flossers, which can be particularly effective in cleaning around dental implants. These tools can help remove debris from hard-to-reach areas, ensuring that implants remain free from harmful bacteria.
By committing to diligent oral hygiene practices, patients can significantly reduce the risk of complications and ensure the effective integration and durability of their dental implants. For further reading on advanced oral hygiene techniques and their benefits, feel free to explore other articles on our website.
Common Questions About Celiac Disease and Oral Health
Celiac disease can have various effects on oral health, which often go unnoticed. Understanding these impacts can help in managing and preventing potential oral health problems.
How does celiac disease affect oral health?
Celiac disease can lead to several dental and oral problems including dental enamel defects, delayed dental development, and canker sores. The autoimmune nature of celiac disease often leads to inflammation, which can affect the mouth and result in conditions such as a dry mouth or a sore, painful tongue. Regular dental check-ups and a strict gluten-free diet can help alleviate these symptoms and improve oral health.

My name is Salman Kapa, a 73-year-old expert in bone regeneration and dental implantology. With decades of experience in the field, I am dedicated to advancing our understanding of oral health and hygiene. Through my research and writing, I aim to contribute to the development of innovative solutions in dental care.