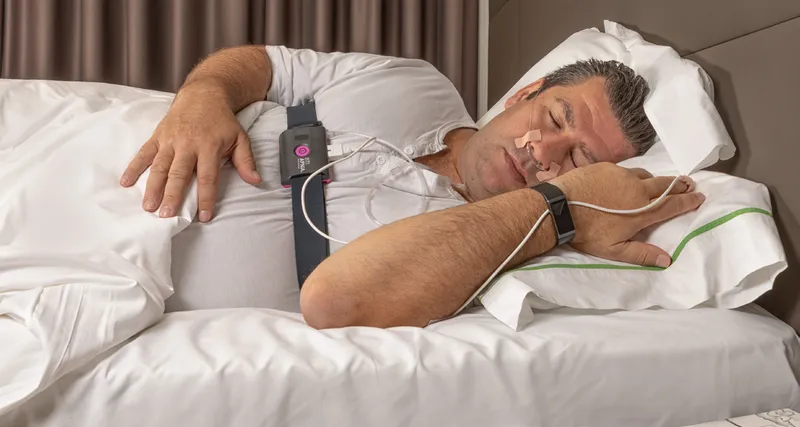
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) machines are widely used for treating sleep apnea, offering numerous benefits like improved sleep quality and reduced daytime fatigue. However, long-term use of CPAP machines may introduce certain side effects. These can include nasal congestion, dryness of the mouth or nose, and occasionally, discomfort from the mask. More rarely, users might experience bloating or even changes in facial structure due to prolonged pressure. Understanding these potential side effects can help users and healthcare providers manage and mitigate them effectively to ensure continued benefit from the therapy.
Common Long-Term Side Effects of CPAP Machines
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) machines are a common and effective treatment for obstructive sleep apnea. While these devices can significantly improve sleep quality and reduce health risks associated with sleep apnea, they can also lead to several long-term side effects. Understanding these potential issues can help users take proactive steps to mitigate them and ensure a more comfortable experience. Some of the most common long-term side effects associated with CPAP machines include skin irritation and sore spots, nasal congestion, and dryness. By addressing these issues early, users can continue to benefit from their CPAP therapy without discomfort.
In this article, we will explore two prevalent long-term side effects of CPAP use: skin irritation and sore spots, and nasal congestion and dryness. Recognizing and addressing these issues can substantially improve your CPAP experience.
Skin Irritation and Sore Spots
One of the most frequently reported side effects of using a CPAP machine is skin irritation and the development of sore spots. The mask must fit snugly to create a seal, but this can sometimes lead to pressure points on the face, particularly around the nose, cheeks, and forehead. Over time, this pressure can cause red marks, soreness, and irritation.
To minimize skin irritation and sore spots, consider the following tips:
- Use a mask liner or cushion to create a barrier between your skin and the mask.
- Adjust the mask straps to ensure a comfortable yet effective fit, avoiding overtightening.
- Regularly clean and replace the mask parts to maintain hygiene and effectiveness.
In some cases, switching to a different type of mask, such as a nasal pillow or a full-face mask, can also alleviate discomfort. It’s crucial to consult with your healthcare provider to find the best solution for your specific situation.
Nasal Congestion and Dryness
Another common side effect of CPAP therapy is nasal congestion and dryness. The continuous airflow can dry out the nasal passages, causing discomfort, congestion, and in some cases, nosebleeds. This issue is particularly prevalent among users who already suffer from allergies or sinus problems.
To combat nasal congestion and dryness, consider the following strategies:
- Use a CPAP machine with a built-in humidifier to add moisture to the air you breathe.
- Apply a saline nasal spray before bedtime to keep nasal passages moist.
- Ensure your mask fits properly to prevent air leaks, which can exacerbate dryness.
Additionally, frequently cleaning the CPAP machine and its components can help prevent the buildup of allergens and irritants that contribute to nasal issues. Consult with your healthcare provider if you continue to experience significant discomfort despite these measures.
If you found this article helpful, you might be interested in reading more about CPAP therapy and other related topics in our other articles. Stay informed and take charge of your sleep health!
Impact on Respiratory Health
The respiratory system is highly susceptible to various influences from both the environment and internal factors. Understanding the impact on respiratory health is crucial for both preventing and managing potential complications. This section delves into the various ways respiratory health can be affected, with a focus on the development of respiratory infections, changes in lung function, and the potential for increased mucus production.
Research has consistently shown that the respiratory system can be significantly impacted by various factors, including exposure to pollutants, infections, and underlying health conditions. Being aware of these factors can help in implementing preventive measures and improving overall respiratory health. Let’s explore the specific aspects that affect the respiratory system in greater detail.
Development of Respiratory Infections
One of the primary concerns regarding respiratory health is the development of respiratory infections. These infections can range from mild colds to severe conditions like pneumonia or bronchitis. The respiratory tract is constantly exposed to pathogens such as viruses, bacteria, and fungi, which can colonize the airways and lead to infections.
Several factors contribute to the susceptibility of respiratory infections, including environmental pollutants, compromised immune systems, and existing chronic diseases. For instance, studies indicate that individuals living in areas with high air pollution levels have a higher incidence of respiratory infections. Additionally, those with weakened immune systems, such as the elderly or individuals with autoimmune conditions, are more prone to developing these infections.
- Avoiding exposure to pollutants
- Maintaining good hygiene practices
- Ensuring proper vaccination
These are some of the essential measures to reduce the risk of respiratory infections. Through understanding these factors, significant strides can be made in improving respiratory health and preventing infections.
Changes in Lung Function
Another significant concern when it comes to respiratory health is potential changes in lung function. Lung function can be measured by parameters such as forced vital capacity (FVC) and forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1). These parameters help in assessing the effectiveness and capacity of the lungs.
Reduction in lung function can result from multiple factors, including chronic exposure to pollutants, genetic predispositions, and lifestyle choices such as smoking. Studies show that smokers, for instance, have a significantly reduced lung function compared to non-smokers. Additionally, chronic conditions such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) can also lead to decreased lung function over time.
Incorporating lifestyle changes can make a substantial difference in preserving lung function. Quitting smoking, reducing exposure to pollutants, and engaging in regular physical exercise are all beneficial strategies. It’s essential to monitor and manage these factors to maintain optimal respiratory health.
Potential for Increased Mucus Production
The potential for increased mucus production is another critical factor affecting respiratory health. Mucus plays a crucial role in trapping pathogens and particles, helping to keep the airways clear. However, excessive mucus production can lead to blockages and difficulty in breathing.
Various conditions can cause increased mucus production, including chronic bronchitis, asthma, and respiratory infections. Chronic bronchitis, a form of COPD, is particularly associated with persistent and excessive mucus production. Allergies can also trigger heightened mucus secretion, contributing to respiratory discomfort and complications.
Managing conditions that lead to increased mucus production involves several strategies:
- Medication to reduce inflammation and mucus secretion
- Hydration to keep the mucus thin and easier to expel
- Avoiding allergens and irritants
By addressing these factors, individuals can significantly improve their respiratory health and manage symptoms more effectively.
Understanding the impact on respiratory health is the first step in improving overall well-being. For more detailed insights, explore our other articles on respiratory care and preventive health measures.
Psychological and Cognitive Effects
The psychological and cognitive effects of oral health, particularly in the context of dental implants and bone regeneration, are profound. The connection between oral health and overall well-being is supported by a growing body of research. The presence of missing teeth or poor oral health can negatively impact an individual’s self-esteem and social interactions, thereby affecting mental health. Conversely, addressing these dental issues through procedures like implants can lead to significant psychological improvements.
Understanding these psychological and cognitive effects demands a multi-faceted approach. Issues such as sleep disturbances, mental health, and cognitive function are all interlinked with overall oral health. By addressing dental needs, we can indirectly aid in improving a patient’s psychological and cognitive well-being. This underscores the importance of a holistic approach to healthcare, where dental health is considered a critical component of overall health.
Sleep Disturbances and Insomnia
Sleep is crucial for maintaining overall health, and disruptions in sleep can have severe repercussions on both psychological and cognitive functions. Research indicates a strong correlation between oral health issues and sleep disturbances. Conditions such as Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) are often linked to dental concerns. Dental implants can help alleviate some of the structural issues that contribute to OSA, thereby improving sleep quality.
Poor oral health and tooth loss can contribute to chronic pain, which in turn can lead to insomnia and other sleep disturbances. The discomfort and pain associated with untreated dental issues can make it difficult for individuals to achieve restorative sleep. By addressing these dental problems through treatments like implants and bone regeneration, patients can experience better sleep, which in turn enhances their cognitive functions and mental health.
Moreover, studies have shown that improving dental health can lead to a reduction in the use of sleep medications. This not only improves the quality of sleep but also reduces the potential side effects and dependency on these medications. Treatment plans that include dental implants can, therefore, be instrumental in addressing sleep-related issues.
Impact on Mental Health
The state of one’s oral health significantly impacts mental health. Conditions like gum disease and tooth loss are often associated with negative self-perception and reduced quality of life. Individuals who suffer from oral health problems might experience feelings of embarrassment, which can lead to social isolation and depression. Dental implants can play a crucial role in restoring confidence and improving social interactions, thereby enhancing mental health.
A study published in the Journal of Clinical Periodontology found a direct link between oral health and mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety. The study highlighted that addressing oral health issues could lead to improvements in mental well-being. Dental implants, by restoring both function and aesthetics, can significantly mitigate these mental health issues.
Additionally, chronic pain from dental issues can contribute to the development of anxiety and depression. By providing a permanent solution like implants, we can reduce the chronic pain and, hence, alleviate the associated mental health problems. It’s not just about fixing teeth; it’s about enhancing overall life quality.
Cognitive Function and Memory Issues
Recent research has highlighted the connection between oral health and cognitive function. Poor oral health, particularly periodontitis and tooth loss, has been associated with a higher risk of cognitive decline and memory issues. The inflammation caused by gum disease can lead to systemic inflammation, which is a risk factor for cognitive impairment.
Dental implants can help reduce the risk of such cognitive issues by addressing the root cause—missing teeth and the resulting bone loss. When teeth are lost, the jawbone begins to deteriorate, which can affect the structure and function of the oral cavity and, consequently, cognitive functions. Implants help maintain the integrity of the jawbone, potentially mitigating cognitive decline.
Moreover, nutritional deficiencies resulting from tooth loss can impact brain health. Individuals with missing teeth may avoid certain nutrient-rich foods, leading to deficiencies that can impair cognitive function. Dental implants restore the ability to chew effectively, allowing for a more balanced diet and better cognitive health. In conclusion, the psychological and cognitive effects of oral health are significant and multifaceted. By addressing oral health issues through procedures like dental implants and bone regeneration, we can contribute to improved sleep, better mental health, and enhanced cognitive functions. Exploring more articles on the intricate link between oral health and overall well-being can provide a deeper understanding of the holistic nature of healthcare.
Understanding the Long-Term Side Effects of CPAP Machines
In exploring the use of Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) machines, particularly for conditions like sleep apnea, it’s essential to consider not only the immediate benefits but also the potential long-term side effects. Here’s a frequently asked question about the long-term use of CPAP machines.
What are common long-term side effects of using a CPAP machine?
While CPAP machines are effective for managing sleep apnea, long-term use can lead to some side effects. Common ones include nasal congestion, dryness of the nose and mouth, skin irritation from the mask, and occasionally, development of pressure sores. Users may also experience bloating and discomfort due to air swallowing, known as aerophagia. Regular consultations with a healthcare provider can help manage these side effects effectively.

My name is Salman Kapa, a 73-year-old expert in bone regeneration and dental implantology. With decades of experience in the field, I am dedicated to advancing our understanding of oral health and hygiene. Through my research and writing, I aim to contribute to the development of innovative solutions in dental care.