Understanding the signs and stages of periodontitis is essential for effective prevention and treatment. This common gum disease not only affects your oral health but can also have a significant impact on your overall well-being. In this article, we explore the initial symptoms, such as swollen or bleeding gums, and the advanced consequences if left untreated. Additionally, we provide practical advice on preventive measures and the latest treatment options available to manage or reverse the condition. With the right care, periodontitis can often be controlled, preventing further dental and health complications.
Understanding Periodontitis
What is Periodontitis?
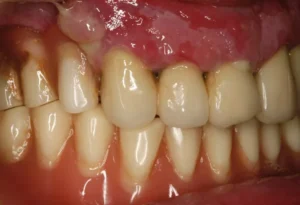
Periodontitis, commonly known as gum disease, is a serious infection that damages the soft tissue and destroys the bone supporting your teeth. If left untreated, periodontitis can lead to tooth loss and increased risk of heart disease. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), nearly half of adults aged 30 and older in the United States have some form of periodontal disease.
The progression of periodontitis begins with the buildup of plaque—a sticky film of bacteria that constantly forms on your teeth. When not removed by brushing and flossing, plaque hardens into tartar that cannot be cleaned by routine brushing and needs a professional dental cleaning. This condition leads to inflammation known as gingivitis, the earliest stage of gum disease. Left untreated, gingivitis can advance to periodontitis, where the inner layer of the gum and bone pull away from the teeth, forming pockets that collect debris and may become infected.
One of the most troubling aspects of periodontitis is that it can be asymptomatic in its early stages. Symptoms like bleeding gums, bad breath, and loose teeth may not appear until significant damage has already occurred. Therefore, regular dental check-ups are crucial for early detection and effective management.
Causes of Periodontitis
Periodontitis is primarily caused by poor oral hygiene. However, several factors can contribute to the development and progression of this disease:
- Poor Oral Care Habits: Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque to build up and harden.
- Smoking: Smoking is one of the most significant risk factors associated with the development of periodontitis.
- Hormonal Changes: Conditions like pregnancy, menopause, and menstruation make gums more sensitive and susceptible to disease.
- Chronic Illnesses: Diseases such as diabetes and rheumatoid arthritis can affect the health and function of your gums.
- Medications: Some drugs reduce saliva flow, making your mouth a more favorable environment for bacteria.
Other factors also play a role, including genetic susceptibility. Some people are more prone to severe periodontitis due to inherited conditions. Moreover, certain nutritional deficiencies, particularly lack of vitamin C, can exacerbate gum problems. Hence, a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle are essential to maintaining periodontal health.
Understanding these causes can significantly help in preventing periodontitis. Employing a consistent oral care regimen and visiting your dentist for regular cleanings and check-ups can make all the difference. Staying informed and proactive in your dental care is the best way to keep periodontitis at bay.
For more in-depth insights into maintaining oral health and preventing periodontitis, be sure to check out our other articles on related topics.
Symptoms of Periodontitis
Periodontitis is a severe gum infection that damages the soft tissue and, if left untreated, can destroy the bone that supports your teeth. It is crucial to recognize the symptoms early to prevent extensive damage. Identifying the signs of periodontitis early can save your teeth and protect your overall health. Below, we discuss both the early signs and the advanced symptoms of periodontitis.
Understanding the symptoms of periodontitis is the first step in addressing this serious oral health issue. Here, we’ll cover the early signs to watch for as well as the advanced symptoms and complications that can arise if the disease progresses without treatment.
Early Signs to Watch For
Early detection of periodontitis can make a significant difference in treatment outcomes. Common early signs include:
- Bleeding gums during brushing or flossing.
- Red, swollen, or tender gums.
- Persistent bad breath (halitosis).
- Gums that seem to be pulling away from the teeth.
Recognizing these symptoms early on can prevent the disease from advancing and causing more severe issues. Another important early sign is the formation of pockets between the teeth and gums. These pockets are spaces where bacteria can accumulate, making it difficult to maintain proper oral hygiene. If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s essential to consult a dental professional promptly.
Advanced Symptoms and Complications
If periodontitis is not treated in its early stages, it can progress to more serious conditions. Advanced symptoms of periodontitis may include:
- Loose or shifting teeth.
- Pus between the teeth and gums.
- Pain while chewing.
- Severe gum recession, revealing more of the tooth.
These symptoms indicate that the infection has damaged the supporting structures of the teeth, including the bone. Left untreated, periodontitis can lead to tooth loss. In addition, research has shown that there may be connections between periodontitis and other systemic health issues, such as heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory problems. This further emphasizes the importance of treating periodontitis promptly.
Complications of advanced periodontitis are not limited to oral health. The chronic inflammation associated with this condition can have systemic effects, contributing to various other health issues. Ensuring timely and effective treatment can help in mitigating these risks and maintaining overall health.
If you’re interested in learning more about maintaining optimal oral health and preventing severe conditions like periodontitis, be sure to check out our other articles. Knowledge is the first step towards a healthy smile!
Preventing Periodontitis
Periodontitis is a severe gum infection that can lead to tooth loss and other serious health complications if not properly managed. By understanding and adopting effective preventive measures, one can significantly reduce the risk of developing this condition. This section will guide you through the essential steps to prevent periodontitis.
Effective prevention of periodontitis revolves around maintaining excellent oral hygiene and visiting your dentist regularly. These methods not only help in keeping your gums healthy but also play a crucial role in your overall well-being.
Daily Oral Care
Daily oral care is the cornerstone of preventing periodontitis. It involves several key practices that, when performed consistently, can greatly reduce the risk of gum disease. The first step is brushing your teeth at least twice a day. Use a toothbrush with soft bristles and fluoride toothpaste to remove plaque and food particles from your teeth and gums.
In addition to brushing, flossing daily is essential. Flossing removes plaque and food particles from between the teeth and under the gumline, areas where a toothbrush cannot reach. Failure to floss can lead to the accumulation of plaque, which is a significant contributor to the development of periodontitis. It’s advisable to use proper flossing techniques to avoid injuring your gums.
Rinsing with an antimicrobial mouthwash can provide an extra layer of protection by reducing the bacteria in your mouth that cause gum disease. Mouthwash can reach areas that brushing and flossing might miss, making it a valuable addition to your daily oral care routine.
Regular Dental Checkups
Visiting your dentist regularly is an essential part of preventing periodontitis. Professional cleanings can remove tartar buildup that at-home oral care cannot eliminate. During these visits, your dentist can also identify early signs of gum disease, allowing for timely intervention.
Most dental professionals recommend a checkup every six months. However, if you have a history of gum disease or other risk factors, such as smoking or diabetes, you may need to visit your dentist more frequently. These regular checkups help in monitoring your oral health and ensuring that any issues are addressed promptly.
During your dental checkup, your dentist will likely perform a comprehensive examination, which includes assessing your gum health. This involves measuring the depth of the pockets around your teeth. Deeper pockets can be a sign of periodontitis. Early detection can prevent the progression of the disease and potentially save your teeth.
In summary, preventing periodontitis requires a combination of meticulous daily oral care and regular professional dental checkups. By incorporating these practices into your routine, you can maintain a healthy smile and avoid the complications associated with gum disease. For more in-depth information on oral health, be sure to explore our other articles.
Understanding Periodontitis: Common Questions Answered
Periodontitis is a serious gum disease that can lead to tooth loss and other health issues. Here are answers to some frequently asked questions to help you understand the symptoms, prevention, and treatment options for periodontitis.
What are the main symptoms of periodontitis?
The main symptoms of periodontitis include swollen and red gums, bleeding when brushing or flossing, bad breath, painful chewing, and loose or sensitive teeth. In advanced stages, you may notice gum recession or pockets between the gums and teeth.
How can periodontitis be prevented?
Preventing periodontitis involves maintaining good oral hygiene. This includes brushing at least twice a day, flossing daily, and visiting the dentist regularly for cleanings and check-ups. Avoiding smoking and managing conditions like diabetes may also help prevent this gum disease.

My name is Salman Kapa, a 73-year-old expert in bone regeneration and dental implantology. With decades of experience in the field, I am dedicated to advancing our understanding of oral health and hygiene. Through my research and writing, I aim to contribute to the development of innovative solutions in dental care.