Sleep choking syndrome, often unrecognized and startling, manifests as a frightening sensation of choking or severe coughing episodes that awaken individuals from sleep. This condition strikes without warning, and though not typically associated with any serious underlying health issues, it can severely disrupt sleep patterns and quality of life. In many cases, it is linked to acid reflux or sleep apnea, both of which cause obstructions or irritations in the airways. Recognizing the symptoms early and consulting with a healthcare provider can lead to effective management strategies, potentially involving lifestyle changes, medical therapy, or interventions to improve respiratory and gastrointestinal health.
Causes of Sleep Choking Syndrome
Sleep choking syndrome, or laryngospasm, is a condition that can cause a person to wake up abruptly during sleep, gasping for air. This distressing experience often leaves individuals feeling anxious and exhausted. Understanding the underlying causes is crucial for effective management and treatment. Several conditions may contribute to sleep choking syndrome, including obstructive sleep apnea, acid reflux, and allergies or sinus problems. Each of these conditions can affect the airway and breathing, leading to the sensation of choking or suffocation during sleep. By identifying and addressing these causes, patients can achieve better sleep quality and overall health. Let’s delve into the specific causes in more detail.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) is a significant cause of sleep choking syndrome. It occurs when the muscles in the throat relax excessively during sleep, causing the airway to become blocked. This blockage can halt breathing multiple times throughout the night, leading to sudden awakenings accompanied by choking or gasping for air. 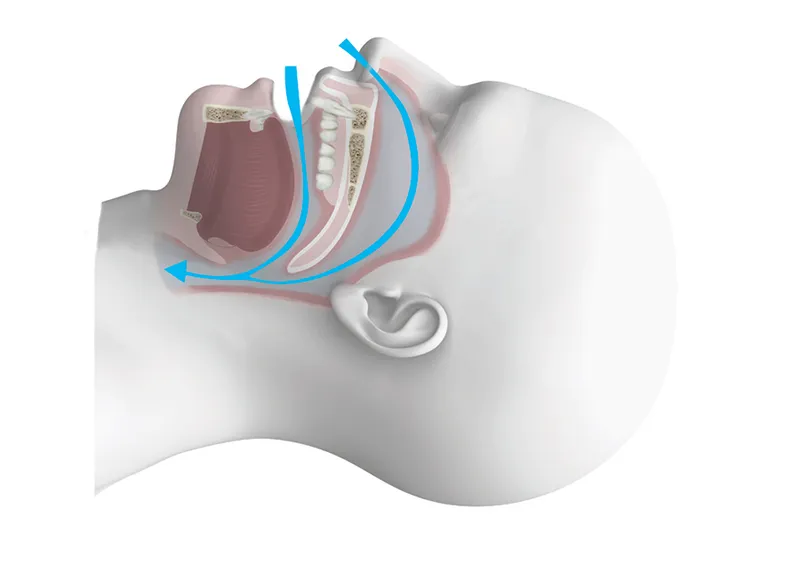
Individuals with OSA often exhibit loud snoring, daytime fatigue, and chronic sleep deprivation. Risk factors for OSA include obesity, a large neck circumference, and certain genetic predispositions. Treating OSA typically involves lifestyle modifications, such as weight loss and the use of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) devices.
Acid Reflux
Acid reflux, or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), is another common cause of sleep choking syndrome. In GERD, stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing irritation and inflammation. When this occurs during sleep, the acid can reach the throat and vocal cords, leading to a choking sensation and abrupt awakenings.
Symptoms of GERD often include heartburn, regurgitation, and a sour taste in the mouth. To manage GERD, patients may need to make dietary adjustments, avoid eating close to bedtime, and take medications to reduce acid production. In severe cases, surgical interventions may be considered.
Allergies and Sinus Problems
Allergies and sinus problems can also contribute to sleep choking syndrome. Allergic reactions and sinus infections can cause nasal congestion and inflammation, leading to difficulty breathing through the nose. As a result, individuals may be forced to breathe through their mouths, increasing the likelihood of airway obstruction and choking sensations during sleep.
Common allergens include pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and mold. Managing allergies often involves taking antihistamines, using nasal sprays, and maintaining a clean living environment. For sinus infections, antibiotics or other treatments may be necessary to alleviate symptoms and reduce the occurrence of sleep choking.
Understanding these underlying causes is vital for those experiencing sleep choking syndrome. By addressing the specific condition contributing to the symptoms, individuals can improve their sleep quality and overall well-being. If you found this article helpful, be sure to explore our other articles on sleep-related topics for more valuable insights.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Understanding the symptoms and diagnosis of dental issues related to implantology and bone regeneration is crucial for timely and effective treatment. Early identification of problems allows for more successful interventions and can prevent complications that might arise from untreated conditions. Diagnostic tools and clinical evaluations play a vital role in this process.
In the realm of dental implants and bone regeneration, symptoms can range from minor inconveniences to severe issues, each requiring different diagnostic approaches. Being aware of these symptoms and knowing how to interpret them can make a significant difference in the outcome of treatment.
Common Symptoms
Patients experiencing problems related to dental implants and bone regeneration may exhibit a variety of symptoms. Some of the most common symptoms include:
- Pain or discomfort in the area of the dental implant, which may indicate an infection or poor fit.
- Swelling and inflammation, which are common post-surgery but should decrease over time. Persistent swelling could be a sign of complications.
- Loose implants, which can occur due to insufficient bone integration or bone loss around the implant.
- Gum recession around the implant site, indicating potential tissue issues or improper healing.
It is essential to monitor these symptoms closely and seek professional advice if any of them persist, as early intervention can prevent more severe complications. For instance, pain and swelling might be managed with antibiotics or anti-inflammatory medications, but persistent issues could require more comprehensive diagnostic evaluations.
These common symptoms often prompt further diagnostic procedures, such as X-rays or CT scans, to assess the condition of the bone and the positioning of the implant. Accurate diagnosis ensures that appropriate treatments are applied, whether they involve medication, surgical intervention, or modifications to existing implants.
Treatments and Management
When it comes to managing and treating dental issues, there are a variety of approaches available depending on the severity and type of the problem. The goal is to not only address the immediate concern but also to prevent further complications. Proper treatment and management often require a combination of lifestyle changes, medication, and medical devices. Understanding these options can help patients make informed decisions about their dental health.
Each treatment modality has its own set of benefits and limitations. It’s essential to discuss these with your dental professional to determine the most suitable plan tailored to your specific needs. Here, we will delve into the primary categories of treatments and management strategies frequently employed in dental care: lifestyle changes, medication, and medical devices.
Lifestyle Changes
One of the most effective and least invasive ways to manage dental issues is through lifestyle changes. Proper oral hygiene practices, such as brushing and flossing regularly, are critical in preventing and managing dental problems. According to the American Dental Association (ADA), brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily can significantly reduce the risk of cavities and gum disease.
Beyond routine dental care, dietary choices also play a crucial role. Consuming a diet low in sugars and high in calcium and vitamins can promote healthier teeth and gums. Foods rich in fiber can naturally clean your teeth, while dairy products provide essential nutrients that strengthen tooth enamel.
Additionally, lifestyle changes such as avoiding tobacco and moderating alcohol consumption can have a significant impact on oral health. Tobacco use is a major risk factor for periodontal disease and oral cancer. Limiting these habits can enhance overall dental health and prevent long-term complications.
Medication
When lifestyle changes alone are insufficient, medications may be required to manage dental issues. Commonly prescribed medications include antibiotics to treat bacterial infections, anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce pain and swelling, and fluoride supplements to strengthen tooth enamel.
Antibiotics, such as amoxicillin, are often prescribed when there is a significant infection that cannot be managed with improved oral hygiene alone. Anti-inflammatory medications like ibuprofen can help alleviate pain from conditions like periodontitis or after surgical procedures.
For patients with a high risk of cavities, fluoride treatments can be particularly beneficial. These treatments come in various forms, including gels, varnishes, and mouth rinses, and they work by making the tooth enamel more resistant to decay.
It’s essential to follow your dentist’s recommendations regarding medication use to ensure the best possible outcomes. Always discuss any potential side effects or interactions with your medications and other health conditions.
Medical Devices
Medical devices are another critical element in the management of dental health, particularly for more severe conditions. Devices such as night guards and orthodontic appliances can prevent damage and correct alignment issues. Night guards, for example, are often used to protect teeth from grinding during sleep, a condition known as bruxism.
Other devices, like dental implants and bridges, can restore function and aesthetics in patients with missing teeth. Dental implants, made from biocompatible materials like titanium, are surgically placed into the jawbone and serve as a strong foundation for artificial teeth.
For patients with obstructive sleep apnea, oral appliances can be a viable alternative to Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) machines. These devices help to keep the airway open during sleep, enhancing comfort and compliance. By incorporating medical devices into a comprehensive treatment plan, patients can achieve better long-term outcomes and improved quality of life. Always consult with a dental professional to determine the most appropriate device for your particular needs.
Understanding the various treatments and management strategies available for dental care can significantly improve your oral health and overall well-being. Be sure to explore our other articles to gain more insights into keeping your smile healthy and bright.
Common Questions About Sleep Choking Syndrome
If you are curious about sleep choking syndrome, here are some frequently asked questions and answers that can provide more insight into this condition.
What exactly is sleep choking syndrome?
Sleep choking syndrome refers to a sleep disorder where individuals experience a sensation of choking or severe difficulty breathing while asleep. This feeling can awaken the person and is often accompanied by a panic feeling due to the inability to breathe properly. It is important to note that, while terrifying, this condition is generally not linked to any blockage of the airway.
What are common triggers for sleep choking syndrome?
This condition may be triggered by several factors including acid reflux, stress, anxiety, and certain sleep-related disorders like sleep apnea. Managing these underlying conditions can often alleviate the symptoms of sleep choking syndrome, improving the quality of sleep and reducing the frequency of episodes.

My name is Salman Kapa, a 73-year-old expert in bone regeneration and dental implantology. With decades of experience in the field, I am dedicated to advancing our understanding of oral health and hygiene. Through my research and writing, I aim to contribute to the development of innovative solutions in dental care.