Sleep disorders encompass a range of issues that affect the ability to sleep well on a regular basis. Whether you’re dealing with insomnia, sleep apnea, or restless legs syndrome, understanding the symptoms is the first step towards management. This article delves into common sleep disturbances, their potential causes, and various treatment strategies aimed at improving sleep quality. Addressing these disorders effectively can significantly enhance overall health and well-being.
Common Symptoms of Sleep Disorders
Sleep disorders are conditions that affect the quality, timing, and amount of sleep, leading to daytime distress and impaired functioning. Recognizing the common symptoms of sleep disorders can help in identifying and seeking timely treatment for these conditions. Below, we will discuss symptoms associated with one of the most prevalent sleep disorders: insomnia.
Patients often do not realize they are struggling with a sleep disorder until it significantly impacts their daily lives. Identifying symptoms early can prevent the condition from becoming more severe and may lead to better overall health outcomes. Sleep disorders can manifest in various ways, depending on the specific disorder, but some general signs are universal.
Insomnia Symptoms
Insomnia is a common
Types of Sleep Disorders
Sleep disorders are a group of conditions that affect the ability to sleep well on a regular basis. They are becoming increasingly common, especially in countries with high levels of stress and fast-paced lifestyles. Recognizing and understanding different types of sleep disorders is crucial for obtaining the appropriate treatment and improving overall quality of life.
Some of the most common types of sleep disorders are insomnia, sleep apnea, and narcolepsy. Each has its unique set of symptoms and underlying causes, and therefore requires distinct approaches for diagnosis and treatment. Below, we delve deeper into these specific sleep disorders.
Insomnia
Insomnia is characterized by difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or both. This condition can lead to daytime drowsiness, lack of energy, and a wide variety of other cognitive and physical problems. It can be classified into two categories: acute insomnia and chronic insomnia.
Acute insomnia is short-term and often occurs because of stressful life events, such as a job loss or a traumatic experience. Generally, it lasts for a few days to a few weeks. Chronic insomnia, on the other hand, occurs at least three times per week and persists for at least three months.
Risk factors for insomnia include high levels of stress, depression, poor sleep habits, and certain medical conditions or medications. Treatment often involves a combination of lifestyle changes, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), and in some cases, medication.
Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a serious sleep disorder where breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep. The most common type is obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), which occurs when the throat muscles intermittently relax and block the airway during sleep. Another type is central sleep apnea, which involves the brain failing to send the proper signals to the muscles that control breathing. Symptoms of sleep apnea include loud snoring, episodes of breathing cessation during sleep, abrupt awakenings accompanied by gasping or choking, and excessive daytime sleepiness. Risk factors include being male, overweight, older age, and having a family history of the disorder.
Treatment for sleep apnea often involves the use of a Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) machine, lifestyle changes such as weight loss, and avoiding alcohol and smoking. In severe cases, surgery may be required to remove tissue and enlarge the airway.
Narcolepsy
Narcolepsy is a chronic sleep disorder characterized by overwhelming daytime drowsiness and sudden attacks of sleep. People with narcolepsy often find it difficult to stay awake for long periods, irrespective of the circumstances. This can lead to significant disruptions in daily life.
One of the most distinctive symptoms is cataplexy, which is a sudden loss of muscle tone that can be triggered by strong emotions. Other symptoms include sleep paralysis and hallucinations during sleep transitions.
While the exact cause of narcolepsy remains unknown, it is believed to be associated with low levels of hypocretin, a neurochemical that regulates wakefulness. Treatment usually involves a combination of medications, such as stimulants to reduce daytime sleepiness, and antidepressants to help manage symptoms like cataplexy.
Understanding these common sleep disorders can empower individuals to seek appropriate medical help and make necessary lifestyle adjustments. For more in-depth information on how to manage sleep disorders, consider exploring our other articles on the topic.
Diagnosis and Evaluation
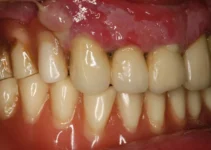
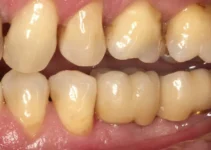
Effective diagnosis and evaluation are at the core of successful dental implantology and bone regeneration. The initial assessment involves a thorough review of the patient’s medical history, dental records, and current health status. This step is crucial to identifying potential risk factors that could affect the outcome of the implant procedure.
Advanced diagnostic tools such as radiographs, CT scans, and intraoral cameras allow for precise evaluation of the patient’s oral anatomy. These tools help in determining the quality and quantity of bone available for the implant, identifying any underlying pathologies, and planning the optimal location for the implant placement.
Moreover, a comprehensive evaluation includes a detailed clinical examination, assessing the condition of the gums, the alignment of the teeth, and the presence of any periodontal diseases or infections. This meticulous approach ensures that the dental implant procedure is safe and tailored to meet the specific needs of the patient.
Medical Tests
Medical tests are an integral component of the diagnosis and evaluation process in dental implantology. Various tests may be conducted to ensure the patient is a suitable candidate for implant surgery and to minimize any risks associated with the procedure.
Blood tests are often carried out to check for underlying systemic conditions like diabetes or hematologic disorders that could impair healing. An optimal healing environment is essential for the success of both the implant and the bone regeneration process.
An alveolar bone density test might be utilized to assess the density and volume of the jawbone. This is crucial as insufficient bone density can compromise the stability and integration of the dental implant.
Additionally, imaging tests such as panoramic X-rays or 3D cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) scans provide detailed images of the jawbone structure. These imaging techniques help in identifying critical anatomical landmarks and potential complications, thus aiding in precise surgical planning.
By incorporating these comprehensive medical tests into the diagnostic process, we can enhance the predictability and success rate of dental implants. For more in-depth information on related topics, be sure to explore our other articles.
Management and Treatment Strategies
Addressing health conditions often requires a multifaceted approach. This is particularly true for chronic conditions, which rarely respond to a single form of treatment. A comprehensive strategy that combines medications, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), and lifestyle changes can significantly improve patient outcomes. Such integrated care is supported by extensive research and clinical experience.
In this section, we will explore the various management and treatment strategies that are commonly recommended. Each approach plays a crucial role in managing the condition effectively. Understanding these methods can help individuals and healthcare providers develop a tailored treatment plan that meets specific needs.
Medications
Medications are often the first line of treatment for many chronic conditions. They can help manage symptoms, slow disease progression, and improve quality of life. Pharmacological treatments are based on extensive clinical trials and have been proven effective in numerous studies. Common medications include:
- Pain relievers: These are essential for managing chronic pain.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs: These help reduce inflammation and pain.
- Antidepressants: Often used in cases where chronic conditions lead to depression.
However, it’s important to remember that medications often come with potential side effects. These can range from mild to severe and should be discussed with a healthcare provider. Regular monitoring and adjustments may be necessary to find the most effective and safe treatment regimen.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a psychological intervention that has gained substantial support for its effectiveness in managing chronic conditions. CBT focuses on changing unhelpful patterns of thinking and behavior that contribute to the patient’s symptoms and overall distress. Studies have shown that CBT can significantly improve mental health outcomes and enhance the effectiveness of other treatments.
CBT typically involves:
- Identifying and challenging negative thought patterns.
- Developing healthy coping mechanisms.
- Setting realistic goals and working towards them progressively.
One of the significant advantages of CBT is its long-term benefits. Unlike medications, which may provide temporary relief, CBT aims to equip patients with the skills needed to manage their condition throughout their lives. Therapy sessions can be conducted individually or in groups, offering flexibility in treatment approaches.
Lifestyle Changes
Incorporating lifestyle changes is another crucial aspect of managing chronic conditions. Simple adjustments can lead to significant improvements in symptoms and overall health. Diet and exercise, for example, are foundational components of a healthy lifestyle and can directly impact the course of many chronic diseases.
Effective lifestyle changes may include:
- Adopting a balanced and nutritious diet.
- Engaging in regular physical activity.
- Ensuring adequate sleep and stress management.
Additionally, avoiding harmful habits like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption is crucial. Lifestyle changes should be tailored to the individual’s specific needs and capabilities, making them easier to maintain over the long run. By understanding and implementing these management and treatment strategies, patients can take proactive steps towards improving their health. For more insights and detailed discussions on related topics, explore our other articles that delve deeper into each aspect of these strategies.
Common Questions About Sleep Disorders
If you’re experiencing issues with your sleep, you might have some questions about what could be causing these problems and how to manage them. Here’s a common query people have about sleep disorders.
What are some typical symptoms of a sleep disorder?
Typical symptoms of a sleep disorder include difficulty falling asleep, frequent awakenings during the night, excessive daytime sleepiness, irregular breathing patterns, or increased movement during sleep. Other signs might include a reduced ability to concentrate, mood disturbances, and decreased performance in work or at school. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for effective management and treatment.

My name is Salman Kapa, a 73-year-old expert in bone regeneration and dental implantology. With decades of experience in the field, I am dedicated to advancing our understanding of oral health and hygiene. Through my research and writing, I aim to contribute to the development of innovative solutions in dental care.