Understanding the significance of early detection of oral cancer can dramatically influence treatment outcomes and survival rates. This type of cancer, which can affect any part of the mouth or the upper throat, is often not diagnosed until it’s in an advanced stage. However, when identified early, treatment options are not only more abundant but also significantly more effective. Symptoms to watch for include persistent sores, unexplained bleeding, numbness, and changes in the mouth’s appearance. Regular visits to a healthcare provider for oral cancer screenings are crucial in catching the disease at its onset, greatly enhancing the chances of successful treatment and recovery.
Understanding Oral Cancer
Oral cancer is a significant health concern that often goes unnoticed until it’s in advanced stages. It encompasses cancers of the mouth, lips, tongue, cheeks, floor of the mouth, hard and soft palate, sinuses, and throat. Being informed about this disease is crucial for early detection and effective treatment. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of oral cancer, including its definition, common symptoms, and risk factors.
A deeper understanding of oral cancer involves recognizing its symptoms and identifying the risk factors. Awareness can prompt timely medical consultation, potentially saving lives. Let’s delve into the specifics of what oral cancer is and the nuances associated with it.

What is Oral Cancer?
Oral cancer, a type of head and neck cancer, arises when there is an uncontrolled growth of cells in the oral cavity. It is commonly classified under squamous cell carcinomas because these cancers typically originate in the flat cells lining the mouth and throat. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), oral cancer is among the top ten most common cancers worldwide. This type of cancer can manifest in various parts of the oral cavity, including the lips, gums, tongue, and the roof or floor of the mouth. Left untreated, it can spread to other parts of the body. Treatment options vary and often depend on the cancer’s stage at diagnosis. Early detection significantly improves the prognosis.
Common Symptoms of Oral Cancer
Recognizing the symptoms of oral cancer early can lead to more successful treatment outcomes. Some of the most common symptoms include:
- Persistent mouth sores that do not heal
- Unexplained bleeding in the mouth
- Red or white patches in the mouth
- A lump or thickening of the cheek
- Difficulty chewing, swallowing, or moving the tongue or jaw
- Numbness or pain in any part of the mouth
If you experience any of these symptoms for more than two weeks, it is crucial to seek professional medical advice. Early intervention can make a significant difference in the treatment success rate.
Risk Factors for Oral Cancer
Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing oral cancer. Understanding these factors can help in adopting preventive measures. Some of the major risk factors include:
- Tobacco use: Smoking cigarettes, cigars, and pipes, as well as using smokeless tobacco, significantly increases the risk.
- Alcohol consumption: Heavy alcohol use is a known risk factor, especially when combined with tobacco use.
- Human papillomavirus (HPV): Certain strains of HPV are associated with oral cancers, particularly those at the base of the tongue and tonsils.
- Age and gender: Men over the age of 50 are at a higher risk compared to women and younger individuals.
- Sun exposure: Prolonged exposure to sunlight can increase the risk of lip cancer.
Other factors such as a poor diet, a weakened immune system, and a family history of cancer can also contribute to the risk. Lifestyle modifications and regular dental check-ups are essential preventive strategies.
Understanding oral cancer is the first step towards prevention and effective treatment. We encourage readers to explore more articles on related topics to stay informed and proactive in their health care.
The Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of dental issues is essential for maintaining optimal oral health. Identifying problems in their initial stages allows for more effective and less invasive treatments. Early intervention can prevent minor issues from developing into significant complications, ultimately saving patients both time and money while ensuring better overall health outcomes.
Moreover, conditions such as periodontal disease and oral cancer can progress silently without noticeable symptoms. By the time symptoms become apparent, the disease may have advanced significantly, necessitating more intensive treatment. Thus, regular dental check-ups and early detection play a crucial role in maintaining long-term oral health.
Benefits of Early Diagnosis
The benefits of early diagnosis in dental care are numerous. When dental issues are detected early, patients can enjoy:
- Minimally invasive treatments: Addressing a small cavity is far simpler and less painful than treating an advanced tooth decay that requires a root canal or extraction.
- Reduced healthcare costs: Treating minor issues early can prevent costly and extensive procedures later on.
- Better prognosis: Early-stage treatment often has a higher success rate and better long-term outcomes.
Furthermore, early diagnoses can lead to better patient education. Patients who are informed about their dental health status can take more proactive steps in their daily care routines, which helps maintain their oral health over the long term. Educating patients about preventive measures and proper oral hygiene practices can significantly reduce the risk of developing more severe dental problems.
Screening Methods
Multiple screening methods are employed to detect dental problems early. These methods help in identifying issues that may not be visible during a standard visual examination. Some of the most effective screening techniques include:
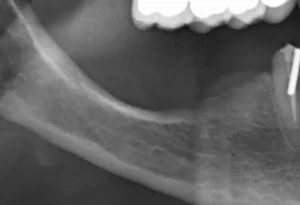
- Dental X-rays: X-rays can reveal hidden decay, bone loss, and structural problems that are not visible during a regular examination.
- Periodontal screening: This involves measuring the depth of gum pockets around the teeth to detect early signs of gum disease.
- Oral cancer screening: Dentists perform a thorough examination of the mouth, including the tongue and the insides of the cheeks, to identify any abnormal lesions or growths.
Advanced technologies such as intraoral cameras and digital imaging have also enhanced the ability of dentists to detect problems early. These tools provide detailed images that can be used to educate patients about their conditions and the necessary treatments.
In conclusion, the importance of early detection in dental care cannot be overstated. Regular screenings and prompt diagnosis not only help in treating problems efficiently but also play a vital role in prevention. For more insights into advanced dental care and treatments, be sure to explore our other articles.
Treatment Options for Oral Cancer
Oral cancer, often referred to as mouth cancer, is a type of head and neck cancer that can affect any part of the oral cavity. Early detection and treatment are crucial for improving survival rates. Various treatment options are available, each tailored to the specific needs of the patient. This article explores the primary treatments used in combating oral cancer. There are three main categories of treatment for oral cancer: surgical treatments, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Each of these treatments may be used alone or in combination, depending on the stage and location of the cancer, as well as the overall health of the patient. Let’s delve deeper into each of these treatment options.
Surgical Treatments
Surgery is often the first line of treatment for oral cancer, especially if the tumor is localized and can be easily accessed. The goal of surgical treatment is to remove the cancerous tissues while preserving as much of the healthy tissue as possible. Common surgical procedures include:
- Resection: Removal of the tumor along with some surrounding healthy tissue to ensure all cancerous cells are eliminated.
- Neck Dissection: If the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes in the neck, these may also need to be removed.
- Reconstructive Surgery: Post-tumor removal, reconstructive surgery may be necessary to restore function and appearance.
Minimally invasive techniques, such as laser surgery and robotic surgery, are also gaining traction as they offer the potential for shorter recovery times and reduced complications. The choice of surgical method depends on the tumor’s size, location, and the patient’s overall health.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays or particles to destroy cancer cells. It can be used as a primary treatment or in conjunction with surgery and chemotherapy. Types of radiation therapy include:
- External Beam Radiation: This is the most common form where radiation is directed at the tumor from outside the body.
- Brachytherapy: Involves placing radioactive material directly inside or near the tumor.
Radiation therapy is especially effective in treating small, localized tumors or in cases where surgery is not feasible. However, it can cause side effects such as dry mouth, sore throat, and changes in taste. Advances in technology, like Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) and Proton Therapy, help target the tumor more precisely, minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing. It is often used in combination with radiation therapy or surgery. Chemotherapy can be administered in different ways:
- Systemic Chemotherapy: Drugs are delivered through the bloodstream to reach cancer cells throughout the body.
- Targeted Therapy: Focuses on specific molecules involved in cancer cell growth, causing fewer side effects than traditional chemotherapy.
Common chemotherapy drugs used for oral cancer include Cisplatin, Fluorouracil (5-FU), and Carboplatin. While effective, chemotherapy can lead to side effects like nausea, fatigue, and lowered immunity. Ongoing research is focused on finding ways to increase the efficacy of chemotherapy while reducing its side effects.
Oral cancer treatment is a multi-faceted approach, and your medical team will tailor a plan that’s right for you. For more insights into managing oral health and understanding various dental treatments, check out our other informative articles.
Key Questions About Early Detection of Oral Cancer
Understanding the significance of early detection can save lives and increase survival rates for those affected by oral cancer. Here’s a common question that sheds light on its importance.
Why is early detection crucial for treating oral cancer?
Early detection of oral cancer significantly improves the prognosis and survival rates. It allows for less invasive treatment options and a higher chance of complete recovery. Detecting oral cancer at an initial stage can help contain the spread of the disease to other areas, reducing the complexity of treatment and associated health complications.

My name is Salman Kapa, a 73-year-old expert in bone regeneration and dental implantology. With decades of experience in the field, I am dedicated to advancing our understanding of oral health and hygiene. Through my research and writing, I aim to contribute to the development of innovative solutions in dental care.