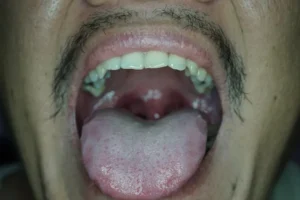
Understanding the signs and appropriate treatments for a tongue infection is crucial for maintaining oral health. A tongue infection can manifest through various symptoms such as swelling, pain, redness, and difficulty swallowing. It may result from various causes, including bacterial, fungal, or viral infections. This article explores common treatments and preventive measures to manage and alleviate the discomfort associated with tongue infections, ensuring a swift recovery and preventing further complications.
Common Symptoms of Tongue Infections
Tongue infections can manifest through a variety of symptoms, some of which are immediately noticeable while others may develop gradually. Understanding these symptoms can help in early diagnosis and treatment, ensuring that the infection does not progress to a more severe state. Let’s explore some of the most common symptoms associated with tongue infections.
It is essential to be aware of these symptoms as they can significantly impact your oral health and overall well-being. If you experience any of the symptoms discussed, consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Pain and Discomfort
Pain is often one of the earliest and most noticeable symptoms of a tongue infection. This pain can range from mild to severe and may be exacerbated by speaking, eating, or swallowing. The discomfort may feel like a burning sensation or a constant throbbing pain.
Discomfort associated with tongue infections often leads to reduced appetite as eating becomes painful. Simple activities like talking or brushing teeth can also become challenging. It is essential to monitor these symptoms and seek medical advice if they persist for more than a few days.
Some common causes of pain and discomfort include infections caused by fungi (such as oral thrush), bacteria, or viruses. Identifying the cause is crucial for effective treatment, whether it involves antifungal, antibacterial, or antiviral medications.
Swelling and Redness
Another prominent symptom of tongue infections is the appearance of swelling and redness. The tongue may appear larger than usual, and you might notice red patches or spots. This swelling can make it difficult to move the tongue freely, affecting speech and eating.
Swelling and redness are often the body’s response to the infection as it tries to fight off invading pathogens. This immune response can sometimes cause further irritation and discomfort.
In some cases, the swelling may also lead to the formation of small, painful blisters or ulcers on the tongue. These sores can increase discomfort and may even bleed in severe cases. Proper diagnosis and treatment are vital to managing these symptoms effectively.
Bad Breath
Bad breath, or halitosis, is another common symptom of tongue infections. This unpleasant odor is usually caused by the bacterial activity on the infected tissue. Bacteria can produce volatile sulfur compounds, leading to bad breath.
Maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial in managing this symptom. Regular brushing, flossing, and the use of mouthwash can help reduce the bacterial load in the mouth. However, if the bad breath persists, it might indicate an underlying infection that needs medical attention.
In addition to bacteria, fungal infections like oral thrush can also lead to bad breath. In such cases, antifungal treatments can help eliminate the infection and improve breath odor.
Identifying and addressing these symptoms early can help prevent complications and ensure effective treatment. If you’re experiencing any of these common symptoms, consult with a healthcare provider. Consider reading more of our articles to stay informed about oral health and related conditions.
Causes of Tongue Infections
Tongue infections can be caused by various factors and present a range of symptoms. Understanding the underlying causes is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment. Among these causes, bacterial infections are a common culprit. Other causes can include fungal infections, viral infections, and even trauma to the tongue. Additionally, systemic conditions such as diabetes and compromised immune systems can also play a role in the development of tongue infections.
In this article, we will delve into the specific causes of tongue infections, with a particular focus on bacterial infections. By understanding the mechanisms through which these infections develop, patients can be better informed and proactive about their oral health. The information presented is based on widely accepted medical research and clinical studies, ensuring that readers receive accurate and reliable information.
Bacterial Infections
Bacterial infections of the tongue are often caused by the overgrowth of bacteria that naturally reside in the oral cavity. These bacteria can proliferate due to poor oral hygiene, leading to infections. Streptococcus and Staphylococcus species are among the most common bacteria responsible for such infections. When oral hygiene is neglected, plaque buildup occurs, creating an environment conducive to bacterial growth and subsequent infection.
Symptoms of bacterial tongue infections can include redness, swelling, and pain. In more severe cases, abscesses may form, accompanied by fever and difficulty swallowing. It is essential to address these symptoms promptly to prevent complications. Treatment typically involves improved oral hygiene practices and, in some cases, antibiotics prescribed by a healthcare professional.
To reduce the risk of bacterial tongue infections, it is recommended to:
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss daily to remove food particles and plaque from between the teeth.
- Use an antibacterial mouthwash as part of your oral hygiene routine.
- Visit your dentist regularly for professional cleanings and check-ups.
Adhering to these practices can significantly decrease the likelihood of developing bacterial infections in the mouth.
In conclusion, bacterial infections are a common cause of tongue infections, but they can be effectively managed and prevented with proper oral care. If you experience persistent symptoms, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Treatment Options for Tongue Infections
Tongue infections can be particularly uncomfortable and, if left untreated, can lead to more serious conditions that affect your overall oral health. A proper diagnosis is essential to determine the most suitable treatment plan. Generally, treatment options can be categorized into professional medical treatments and home remedies. Understanding the underlying cause of the infection is key to selecting the most effective treatment.
Infections on the tongue may be caused by bacteria, fungi, or viruses, with each requiring a different treatment approach. Professional medical treatments often include prescription medications, while home remedies can provide relief and support healing. It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider to ensure that the chosen treatment is appropriate for your specific condition.
Whether opting for antibiotic therapy or trying out home remedies, maintaining good oral hygiene and following your dentist’s advice will speed up the recovery process. Here, we’ll discuss the most common treatment options available to help you manage and cure tongue infections effectively.
Antibiotic Therapy
Antibiotic therapy is commonly prescribed when a bacterial infection is identified as the cause of the tongue infection. These infections often occur due to poor oral hygiene, trauma, or an underlying health condition that compromises the immune system. Antibiotics work by targeting the bacteria causing the infection, thereby reducing inflammation and preventing the spread of the infection. When prescribed antibiotics by a healthcare provider, it is crucial to follow the dosage and duration recommendations closely. Overuse or misuse of antibiotics can lead to antibiotic resistance, making future infections harder to treat. In some cases, a combination of antibiotics may be necessary to effectively fight off the infection.
Antibiotics may be administered in various forms, such as oral tablets, topical gels, or even injections, depending on the severity of the infection. It is essential to complete the entire course of antibiotics even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication. Stopping treatment prematurely can result in a resurgence of the infection.
Home Remedies
Home remedies can be an effective complementary treatment to professional medical interventions or as a first line of defense against mild infections. These remedies often focus on alleviating symptoms and promoting a healthy environment in the mouth to aid in recovery. It’s important to note that home remedies should not replace professional medical advice but can be beneficial for mild cases or additional support. Common home remedies for tongue infections include:
- Saltwater Rinse: Salt has natural antiseptic properties that can help reduce bacterial load in the mouth. Rinsing with a saltwater solution multiple times a day can provide relief and promote healing.
- Hydrogen Peroxide: Diluting hydrogen peroxide with equal parts water and using it as a mouthwash can help disinfect the infected area.
- Yogurt: Consuming yogurt with live cultures can help restore the balance of good bacteria in the mouth, which can be particularly helpful if the infection is fungal in origin.
- Aloe Vera Gel: Applying aloe vera gel directly to the infected area can reduce inflammation and promote healing.
Maintaining good oral hygiene, including brushing and flossing regularly and avoiding irritants such as spicy foods, can also play a significant role in managing tongue infections. Drinking plenty of water helps to keep the mouth hydrated and wash away harmful bacteria.
For more detailed insights on how to improve your oral health and prevent future infections, be sure to explore our other articles. Your journey to a healthier mouth starts with staying informed and proactive.
Common Questions About Tongue Infections
If you’re experiencing symptoms or problems with a tongue infection, you may have several questions about what is happening and how to treat it. Below is a frequently asked question to help you understand more about this condition.
What are the common causes of tongue infections?
Tongue infections can be caused by a variety of factors, including fungal infections like oral thrush, viral infections such as herpes simplex virus, and bacterial infections. Poor oral hygiene, wearing dentures, smoking, a weakened immune system, and certain medical conditions like diabetes can also increase the risk of developing an infection of the tongue.

My name is Salman Kapa, a 73-year-old expert in bone regeneration and dental implantology. With decades of experience in the field, I am dedicated to advancing our understanding of oral health and hygiene. Through my research and writing, I aim to contribute to the development of innovative solutions in dental care.