A tooth infection, medically known as an abscessed tooth, can significantly impact oral and overall health if not treated promptly. This condition arises when bacteria invade the dental pulp, leading to inflammation and infection. Common signs include severe pain, swelling, and sensitivity to temperature. Beyond maintaining rigorous dental hygiene, it’s imperative to seek immediate professional care to prevent the spread of infection and ensure thorough treatment. Understanding the underlying causes and adopting preventive measures can drastically reduce the risk of developing such infections.
Causes of Tooth Infection
Tooth infections can occur due to a variety of reasons, but they are most commonly the result of bacterial invasion into the tooth’s structure. Once bacteria penetrate the tooth’s protective layers, they can cause significant damage and pain. Understanding the primary causes of tooth infection is crucial for both prevention and treatment.
In this section, we will explore two of the most common causes: bacterial invasion and tooth decay. Both of these factors can lead to serious dental issues if not addressed promptly and effectively.
Bacterial Invasion
Bacterial invasion is one of the primary causes of tooth infections. Bacteria are always present in the mouth, but they can become problematic when they invade the inner structures of the teeth. This usually happens when the protective enamel is compromised due to cracks, chips, or decay. Once inside, bacteria can multiply rapidly, causing an infection.
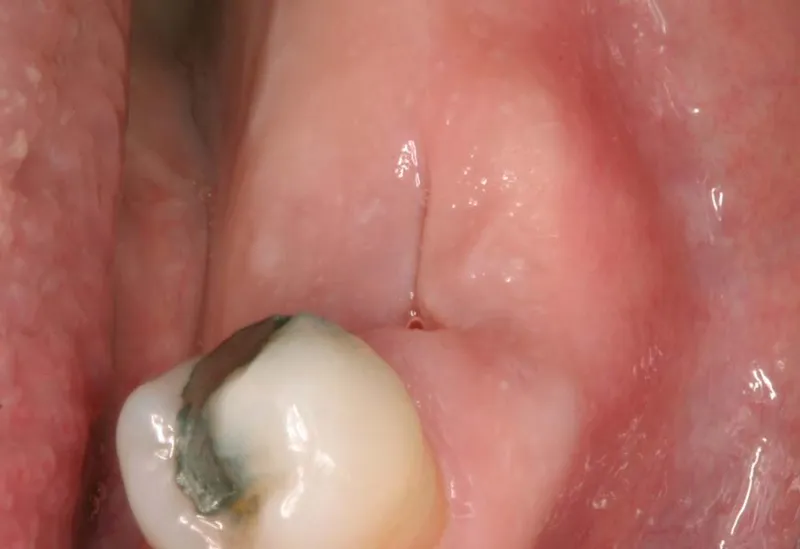
One of the most common forms of bacterial invasion is a dental abscess, which is a pocket of pus that forms due to bacterial infection. This can be extremely painful and often requires immediate medical attention. Abscesses can form in different parts of the tooth and gum, including:
- Periapical Abscess: Forms at the tip of the tooth’s root
- Periodontal Abscess: Occurs in the gums next to a tooth root
Prevention of bacterial invasion involves maintaining good oral hygiene, such as brushing and flossing regularly, and visiting the dentist for routine check-ups. Antibiotics are often required to treat severe cases of bacterial infection.
Tooth Decay
Tooth decay is another leading cause of tooth infections. It occurs when the enamel and dentin layers of the tooth are eroded by acids produced by bacteria in the mouth. These acids form when sugary and starchy foods are broken down. Over time, the acidic environment leads to the formation of cavities, which can become infected if left untreated.
Tooth decay can progress through several stages, starting from minor enamel erosion to severe tooth decay, leading to infection. The stages of tooth decay include:
- Initial Demineralization: The outer enamel begins to weaken
- Decay of Enamel: Cavities start to form
- Dentin Decay: Bacteria penetrate deeper into the tooth
- Pulp Damage: The inner pulp becomes infected
Preventing tooth decay involves a combination of good dental hygiene practices and dietary choices. Brushing twice a day, flossing, and reducing the intake of sugary foods can significantly lower the risk of decay. Fluoride treatments and dental sealants can also provide additional protection. In severe cases where decay has led to infection, treatments such as root canals or extractions may be necessary. These procedures help to remove the infected tissue and restore the health of the tooth and surrounding gums.
Understanding the causes of tooth infection can guide you in taking preventive measures and seeking timely treatment. Explore our other articles to learn more about oral health and how to maintain a healthy, infection-free mouth.
Symptoms of Tooth Infection
Tooth infections, or dental abscesses, are serious conditions that require prompt attention. They manifest in various ways, and recognizing the symptoms early can make a significant difference in treatment outcomes. Below, we explore some common symptoms of tooth infections to help you identify and seek treatment promptly.
Understanding these symptoms will not only help in early detection but also prevent the infection from spreading to other parts of the body, which can be life-threatening. Here are some key indicators of a tooth infection:
#img_2##
Severe Toothache
A severe toothache is often the most noticeable and painful symptom of a tooth infection. This pain can be persistent and throbbing, and it might radiate to the jawbone, neck, or ear. The pain can worsen when lying down, making it difficult to get a good night’s sleep.
The toothache associated with an infection is typically more intense than usual dental discomfort. You may also experience sensitivity to hot and cold temperatures, making it uncomfortable to consume certain foods and beverages. Over-the-counter pain relievers may offer temporary relief, but they won’t address the underlying infection. If you experience a severe toothache that doesn’t subside within a couple of days, it’s crucial to seek dental attention immediately. Ignoring the pain can lead to further complications, including the spread of the infection.
Swelling in the Gums
Swelling in the gums is another common symptom of a tooth infection. This swelling, also known as gum abscess, usually occurs near the infected tooth. The area may appear red, inflamed, and feel tender to the touch. In some cases, you might notice a pimple-like bump on the gum that’s filled with pus.
The swelling can cause significant discomfort and affect your ability to eat, speak, or even smile. It can sometimes be accompanied by a foul taste in the mouth if the abscess ruptures, releasing the pus.
Early intervention by a dental professional can help drain the abscess and eliminate the infection. If left untreated, the infection can spread to adjacent teeth, jawbones, and even enter the bloodstream, posing serious health risks.
Fever and Malaise
A fever is the body’s natural response to fighting an infection, including a tooth infection. If you have a dental abscess, you might experience an elevated body temperature, chills, and general malaise. These systemic symptoms indicate that the infection has progressed and is affecting your overall health.
Malaise refers to a general feeling of discomfort, illness, or unease. You may feel fatigued, weak, and find it difficult to perform daily activities. In severe cases, the infection can lead to nausea and dizziness.
Experiencing fever and malaise in conjunction with other symptoms like severe toothache and gum swelling necessitates urgent dental care. These symptoms suggest that the infection is not localized and could have serious implications for your health.
Recognizing the symptoms of a tooth infection is the first step toward seeking prompt and effective treatment. If you think you may have a tooth infection, it’s important to contact a dental professional as soon as possible. For more detailed information on dental health and treatments, be sure to explore our other articles.
Prevention Strategies for Tooth Infection
Maintaining Proper Oral Hygiene
One of the most effective ways to prevent tooth infections is by maintaining proper oral hygiene. This includes consistently practicing good brushing and flossing techniques. Brushing your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste helps remove plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that can lead to infections. Flossing is equally important as it removes food particles and plaque from between the teeth and under the gumline where a toothbrush can’t reach.
Using an antimicrobial mouthwash can also enhance your oral hygiene routine. These mouthwashes help reduce bacteria that cause tooth decay and gum disease. Additionally, replacing your toothbrush every three to four months, or sooner if the bristles become frayed, ensures that you are not reintroducing bacteria into your mouth.
Proper oral hygiene doesn’t stop at your daily routine. Avoiding habits like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption is also crucial, as these can contribute to oral health issues. Smoking, in particular, has been linked to a range of dental problems, including gum disease, which can increase the risk of tooth infection.
Regular Dental Check-ups
Regular dental check-ups are a cornerstone of preventing tooth infections. Dentists recommend that you visit them at least twice a year for a thorough cleaning and examination. These visits allow your dentist to identify early signs of decay or infection and address them before they become more serious.
During these check-ups, your dentist can also take X-rays to see areas that are not visible during routine examinations. This can help in detecting hidden dental issues, such as abscesses, cysts, or impacted teeth, which could potentially lead to infection if left untreated.
Professional cleanings performed by dental hygienists help remove hardened plaque (tartar) that cannot be removed by regular brushing and flossing. These cleanings are essential in maintaining gum health and preventing periodontal disease, a major cause of tooth infection.
Balanced Diet
A well-balanced diet plays a significant role in maintaining oral health and preventing tooth infections. Consuming a diet rich in vitamins and minerals helps keep your teeth and gums healthy. Calcium, found in dairy products and leafy greens, strengthens tooth enamel, while vitamin C, found in fruits and vegetables, supports gum health.
Limiting the intake of sugary foods and beverages is crucial. Bacteria in the mouth feed on sugar, producing acids that can erode tooth enamel and lead to cavities and infections. It’s also wise to avoid sticky foods that cling to your teeth, as they provide a prolonged food source for bacteria.
Staying hydrated is another important aspect of a balanced diet. Drinking plenty of water helps wash away food particles and bacteria, reducing the risk of tooth decay. Saliva production, which is essential for neutralizing acids and protecting teeth, is also stimulated by adequate water intake.
Incorporating fibrous foods like fruits and vegetables into your diet can help clean your teeth naturally and keep your gums healthy. Chewing these foods stimulates saliva production, which further aids in protecting your teeth from decay and infection.
Treatments for Tooth Infection
Tooth infections, also known as dental abscesses or periapical abscesses, are serious conditions that require prompt and effective treatment. The primary goal of treating a tooth infection is to eliminate the infection, relieve pain, and prevent further complications. Understanding the available treatment options helps in making informed decisions regarding dental health. Here, we will discuss three common treatments for tooth infections: Antibiotics, Root Canal Therapy, and Tooth Extraction.
It’s important to recognize the signs of a tooth infection which include severe toothache, sensitivity to hot or cold, swelling of the face or cheek, and fever. If left untreated, a tooth infection can lead to serious complications such as the spread of infection to other parts of the body. Early intervention is crucial, and a dentist will choose the most appropriate treatment based on the severity of the infection and the specific circumstances of the patient.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are often prescribed to treat bacterial infections, including those affecting the teeth. They work by killing the bacteria causing the infection or inhibiting their growth. While antibiotics can be very effective, they are usually not a standalone solution for dental abscesses. They are typically used when:
- The infection is localized but there’s swelling and fever.
- The patient cannot undergo immediate dental treatment.
- The infection is spreading or poses a risk of spreading.
However, it’s important to use antibiotics judiciously to avoid the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. A dentist will often prescribe antibiotics as a complementary treatment to either root canal therapy or tooth extraction. Patients should follow the dosage instructions carefully and complete the full course of antibiotics even if symptoms improve.
Root Canal Therapy
Root canal therapy is a common and effective procedure for treating tooth infections that affect the pulp of the tooth. The pulp is the innermost part containing nerves and blood vessels. When the pulp becomes infected, it can cause severe pain and lead to the formation of an abscess. Root canal therapy involves:
- Removing the infected or damaged pulp.
- Cleaning and disinfecting the interior of the tooth.
- Filling and sealing the tooth to prevent further infection.
This procedure helps save the natural tooth, which is always preferable to extraction. It also alleviates pain and restores the tooth’s function. Advances in dental techniques and anesthesia have made root canal therapy a relatively comfortable procedure, with high success rates.
Tooth Extraction
In cases where the tooth is severely damaged or the infection is extensive, tooth extraction may be necessary. This procedure involves removing the tooth entirely to prevent the infection from spreading. Tooth extraction is typically considered when:
- The tooth cannot be saved through root canal therapy.
- The infection persists despite other treatments.
- The tooth is causing severe pain and compromising the patient’s health.
While the idea of losing a tooth can be daunting, modern dental practices offer several options for tooth replacement, such as dental implants, bridges, or dentures. These alternatives can restore both function and aesthetics. Following the extraction, it’s important to maintain good oral hygiene and follow post-operative care instructions to ensure proper healing.
Understanding these treatment options can help individuals make informed decisions and seek timely dental care. For more in-depth information on related topics, we recommend exploring our other articles on dental health and treatments.
Common Questions About Tooth Infections
If you’re concerned about tooth infections, understanding more about them can help you prevent and manage this dental problem effectively.
What are the typical signs of a tooth infection?
Typical signs of a tooth infection include severe toothache with persistent pain, sensitivity to hot and cold, swelling in the cheek, bad breath, and sometimes fever. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s crucial to consult a dentist promptly to prevent the spread of the infection.

My name is Salman Kapa, a 73-year-old expert in bone regeneration and dental implantology. With decades of experience in the field, I am dedicated to advancing our understanding of oral health and hygiene. Through my research and writing, I aim to contribute to the development of innovative solutions in dental care.