Temporomandibular joint dysfunction, commonly referred to as TMJ, affects countless individuals, causing discomfort and impaired jaw function. This condition can manifest as pain in the jaw joint and surrounding muscles, potentially impacting one’s ability to speak, chew, and swallow effectively. Various treatment options exist ranging from lifestyle adjustments and physical therapy to more advanced interventions such as dental appliances or even surgery. Early diagnosis and a tailored treatment plan are crucial for alleviating symptoms and preventing long-term complications.
What is Temporomandibular Joint Dysfunction?
The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) serves as the connection between the jawbone and the skull. Any dysfunction in this joint can result in significant discomfort and disability. Temporomandibular Joint Dysfunction (TMJD) encompasses a range of issues related to this joint, including pain, restricted movement, and audible sounds during jaw activities.
TMJD is a complex and multifactorial condition that involves both muscular and joint-based factors. It can be triggered by various elements such as injury, arthritis, or habitual behaviors like teeth grinding. Understanding its etiology and recognizing its symptoms are crucial for effective treatment and management.
Definition of TMJ Dysfunction
Temporomandibular Joint Dysfunction (TMJD) refers to a collection of conditions affecting the TMJ and the muscles controlling jaw movement. TMJD can manifest as pain in the jaw, face, neck, and even shoulders, making it a comprehensive condition to diagnose and treat.
There is often a lack of consensus on the specific definition of TMJD due to its multifactorial nature. However, it generally involves a combination of musculoskeletal problems, often exacerbated by psychological issues like stress and anxiety. Common contributing factors include:
- Dislocation or injury to the jaw
- Arthritis in the TMJ
- Chronic grinding or clenching of teeth
- Structural abnormalities
Common Symptoms of TMJ Dysfunction
The symptoms of TMJD can vary widely from person to person. They often include a combination of physical and psychological discomforts. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent pain or tenderness in the jaw
- Aching pain around the ear
- Difficulty chewing or discomfort while chewing
- Locking of the TMJ, making it difficult to open or close the mouth
- Unexplained headaches
Other symptoms may involve clicking or popping sounds when opening or closing the mouth, earaches, and even dizziness. Because these symptoms can mimic other conditions, accurate diagnosis often requires a thorough examination and sometimes imaging studies like X-rays or MRIs.
Understanding the broad spectrum of symptoms associated with TMJD can help in early detection and treatment, significantly improving the quality of life for affected individuals. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is crucial to consult with a dental specialist to rule out other potential issues and to receive targeted treatment.
For more insights into dental health, be sure to read our other articles covering topics such as oral hygiene, dental implants, and the latest in regenerative dental technology.
Causes of Temporomandibular Joint Dysfunction
Temporomandibular Joint Dysfunction (TMD) is a condition that affects the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), which connects the jawbone to the skull. The causes of TMD are varied and can be broadly separated into physical and psychological factors. Understanding the root causes of TMD is crucial for effective treatment and management. Studies indicate that nearly 10 million Americans suffer from TMD, underscoring the importance of identifying and addressing the underlying causes. While some risk factors are evident, like jaw injuries, others may not be as obvious, including stress and anxiety.
The interplay of physical and psychological causes makes TMD a complex disorder requiring a multidisciplinary approach for effective treatment. Let’s delve into these causes in more detail to enhance our understanding and management of this condition.
Physical Causes
Physical causes of TMD are often linked to issues such as trauma or injury to the jaw, head, or neck. Sports injuries, car accidents, or even simple falls can lead to damage that impacts the TMJ. Additionally, conditions such as arthritis can contribute to TMD by affecting the cartilage within the joint.
Other physical factors include bruxism (teeth grinding) and clenching of the jaw, which can lead to wear and tear on the TMJ. Malocclusion, or the misalignment of teeth, is another significant cause that can place undue stress on the joint.
- Jaw injuries from accidents
- Arthritis affecting TMJ cartilage
- Bruxism (teeth grinding)
- Jaw clenching
- Malocclusion (misaligned teeth)
It’s essential for patients experiencing symptoms of TMD to consult with a healthcare provider for a comprehensive assessment and to identify any physical causes that may require targeted treatment.
Psychological Causes
Psychological factors can also play a significant role in the development and exacerbation of TMD. Stress and anxiety are known contributors to muscle tension and bruxism, which, in turn, can impact the TMJ. People under chronic stress may unconsciously clench their jaw or grind their teeth, leading to TMD over time.
Emotional trauma and mental health conditions, such as depression, can also be linked to TMD. The body’s response to emotional stress often involves physical manifestations, including tension in the jaw muscles, which can exacerbate TMD symptoms.
Managing these psychological factors through therapy, stress management techniques, and sometimes medication can be an integral part of a comprehensive TMD treatment plan. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and mindfulness practices have shown promise in reducing symptoms in patients with stress-related TMD.
In conclusion, both physical and psychological causes contribute to TMD. Effective treatment often involves addressing both aspects to provide relief from symptoms and improve the quality of life for those affected. For more in-depth information on related topics, be sure to read our other articles.
Treatment Options for Temporomandibular Joint Dysfunction
Temporomandibular Joint Dysfunction (TMD) can cause significant discomfort and pain, impacting the overall quality of life. Managing TMD effectively requires a thorough understanding of the underlying causes and tailored treatment strategies. Treatment options can be broadly categorized into non-surgical and surgical treatments, with the approach depending on the severity of the condition and the patient’s specific needs.
Many patients benefit from a combination of treatments designed to alleviate symptoms while addressing the root cause of their dysfunction. Consulting with a specialized dental professional can help determine the most appropriate course of action for each individual case. Understanding the available treatment options is crucial for making informed decisions about TMD management.
Non-Surgical Treatments
Non-surgical treatments are typically the first line of defense against TMD and can be quite effective for many patients. These treatments focus on reducing pain and improving the function of the jaw joint without invasive procedures. Common non-surgical treatments include:
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to strengthen jaw muscles and improve range of motion.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and muscle relaxants.
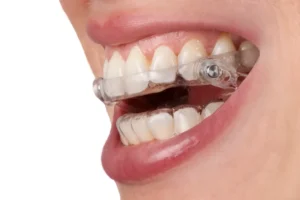
- Oral Appliances: Custom-made splints or mouthguards to reduce teeth grinding and relieve pressure on the jaw.
Physical therapy often involves techniques such as heat and cold therapy, ultrasound, and targeted exercises. These methods aim to reduce inflammation, relax the muscles, and restore normal joint function. Medications can provide temporary relief from pain and inflammation, allowing the patient to engage more effectively in physical therapy and other non-surgical treatments. Oral appliances, such as splints and mouthguards, are designed to reposition the jaw and alleviate stress on the temporomandibular joint. These devices can be particularly useful for patients who grind their teeth or have a misaligned bite. By reducing the strain on the jaw, oral appliances allow the joint to heal and function more efficiently.
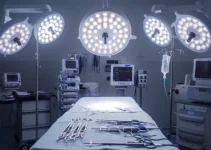
Surgical Treatments
For patients with severe TMD who do not respond to non-surgical treatments, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgical treatments aim to repair or reposition the temporomandibular joint to restore normal function and alleviate pain. Common surgical options include:
- Arthrocentesis: A minimally invasive procedure to remove debris and inflammatory byproducts from the joint.
- Arthroscopy: A slightly more invasive procedure that uses a small camera to visualize and treat joint issues.
- Open Joint Surgery: A more extensive procedure to repair or replace the joint for severe cases.
Arthrocentesis involves injecting fluid into the joint to wash out inflammatory products and debris, reducing pain and improving joint function. This procedure is relatively simple and can provide significant relief for patients with moderate TMD symptoms. Arthroscopy, on the other hand, involves the use of a small camera and surgical instruments inserted through tiny incisions to diagnose and treat joint problems directly.
Open joint surgery is considered when less invasive methods fail to provide relief. This procedure allows the surgeon to directly access the temporomandibular joint to repair or replace damaged tissue. While it is more invasive, open joint surgery can be highly effective for patients with severe TMD who require significant intervention to restore normal joint function.
Understanding the full spectrum of treatment options for TMD is essential for patients seeking relief from this debilitating condition. By exploring both non-surgical and surgical treatments, patients and their healthcare providers can develop a comprehensive plan tailored to the individual’s needs.
For more information on managing TMD and other dental health topics, be sure to explore our other articles and resources.
What is Temporomandibular Joint Dysfunction and How to Treat It
Temporomandibular joint dysfunction (TMJD) affects millions each year, causing pain and discomfort in the jaw area. Below is a common question answered to provide clarity on this condition and its management.
What is temporomandibular joint dysfunction and how can it be treated?
Temporomandibular joint dysfunction is a disorder that affects the joint connecting the jawbone to the skull, leading to pain, difficulty chewing, and noise during jaw movement. Treatment varies depending on the severity and cause. Common methods include physical therapy, exercises to relax and strengthen jaw muscles, medications like pain relievers or anti-inflammatories, bite guards or splints to reduce clenching and grinding, and in some severe cases, surgical interventions may be considered to repair or improve joint function.

My name is Salman Kapa, a 73-year-old expert in bone regeneration and dental implantology. With decades of experience in the field, I am dedicated to advancing our understanding of oral health and hygiene. Through my research and writing, I aim to contribute to the development of innovative solutions in dental care.